What is the length of the side marked X?
Using the Pythagorean Theorem: Calculate The Missing Side based on the formula
What is the length of the side marked X?
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find BC
\( \)
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find AB
Look at the triangle in the diagram. How long is side BC?
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find AB
Examples with solutions for Using the Pythagorean Theorem: Calculate The Missing Side based on the formula
Exercise #1
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
We use the Pythagorean theorem:
Answer
Exercise #2
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find BC
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve this problem, we'll perform the following steps:
Step 1: Identify the sides of the triangle. The problem states and . Since triangle ABC is a right triangle, is the hypotenuse.
Step 2: Apply the Pythagorean Theorem, which states , where is the hypotenuse.
Step 3: In this case, set , , and . Substitute these into the theorem:
Step 4: Calculate and . Thus, the equation becomes:
Step 5: Rearrange to solve for :
Step 6: Solve for by taking the square root:
Therefore, the length of side BC is .
Answer
Exercise #3
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find AB
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve the problem, we will use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the length of side . According to the theorem, .
Given:
- Hypotenuse
- One leg
We need to find :
Solve for :
By subtracting 1 from both sides:
Taking the square root of both sides gives us:
Therefore, the length of side is .
Answer
Exercise #4
Look at the triangle in the diagram. How long is side BC?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve the exercise, it is necessary to know the Pythagorean Theorem:
A²+B²=C²
We replace the known data:
2²+B²=7²
4+B²=49
We input into the formula:
B²=49-4
B²=45
We find the root
B=√45
This is the solution. However, we can simplify the root a bit more.
First, let's break it down into prime numbers:
B=√(9*5)
We use the property of roots in multiplication: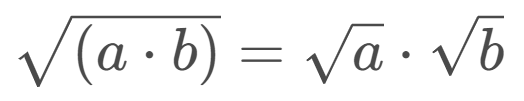
B=√9*√5
B=3√5
This is the solution!
Answer
cm
Exercise #5
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find AB
Step-by-Step Solution
To find the length of side in the right triangle , we will use the Pythagorean Theorem. The theorem is given by:
In this equation, is the hypotenuse, and and are the other two sides. Based on the given information, we have:
- is one leg.
- is the hypotenuse.
- is the unknown leg we want to find.
Substituting the known values into the Pythagorean Theorem:
Simplifying the equation:
Subtract 36 from both sides to solve for :
To find , take the square root of both sides:
Therefore, the length of side is .
Answer
Given the triangle ABC, find the length BC
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find \( X \)
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find BC
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find AB
\( \)
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find AB
Exercise #6
Given the triangle ABC, find the length BC
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
To answer this question, we must know the Pythagorean Theorem
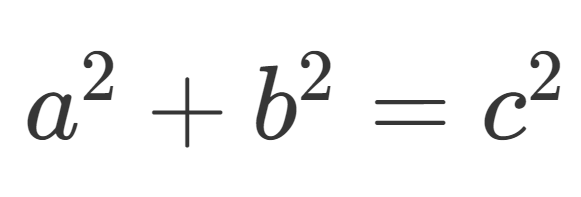
The theorem allows us to calculate the sides of a right triangle.
We identify the sides:
ab = a = 5
bc = b = ?
ac = c = 13
We replace the data in the exercise:
5²+?² = 13²
We swap the sections
?²=13²-5²
?²=169-25
?²=144
?=12
Answer
12 cm
Exercise #7
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve the given problem, we will use the Pythagorean Theorem, which is stated as:
Here, represents the hypotenuse, and and are the legs of the right triangle. Based on our problem:
- (the hypotenuse)
- (one of the legs)
- (the missing side we need to find)
Applying the Pythagorean theorem, we get:
Calculating the squares, we have:
Subtracting 25 from both sides to isolate :
Taking the square root of both sides to solve for :
Therefore, the solution to the problem is , which corresponds to choice 1 in the multiple-choice answers.
Answer
Exercise #8
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find BC
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve for in the right triangle , we follow these steps:
- Identify the given lengths: and .
- Apply the Pythagorean Theorem: .
- Substitute known values into the formula:
Simplify the left side:
Subtract 36 from both sides:
Solve for by taking the square root of both sides:
Thus, the length of is .
Answer
Exercise #9
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find AB
Step-by-Step Solution
To find the length of side AB in the right triangle ABC:
- Step 1: Identify the known lengths. We know and .
- Step 2: Apply the Pythagorean Theorem: .
- Step 3: Plug in the known values: .
- Step 4: Since , the equation becomes .
- Step 5: Subtract 36 from both sides, yielding: .
- Step 6: Take the square root of each side: .
Thus, the length of side AB is .
Answer
Exercise #10
Triangle ABC is a right triangle,
Find AB
Step-by-Step Solution
To find the length of side in the right triangle , we will use the Pythagorean theorem:
Since is the hypotenuse, , and one leg , we can express the Pythagorean theorem as:
Substituting the known values gives us:
Simplifying further:
Subtracting 25 from both sides results in:
Taking the square root of both sides, we obtain:
Therefore, the length of side is .
Answer
Look at the following rectangle:
AB = 12
AC = 13
Calculate the area of the triangle BCD.
Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle ABCD.
Look at the triangle in the figure.
What is the length of the hypotenuse given that its perimeter is \( 12+4\sqrt{5} \) cm?
Exercise #11
Look at the following rectangle:
AB = 12
AC = 13
Calculate the area of the triangle BCD.
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve this problem, we'll follow these steps:
- Step 1: Use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the length of .
- Step 2: Calculate the area of triangle .
Step 1: Given and , we use the Pythagorean Theorem to find .
Step 2: Knowing the sides (height of the rectangle) and (base of the rectangle), triangle will have the base and the height .
The area of triangle is:
Therefore, the area of triangle is 30.
Answer
30
Exercise #12
Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle ABCD.
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
Let's focus on triangle BCD in order to find side BC.
We'll use the Pythagorean theorem using our values:
Let's now remove the square root:
Since each pair of opposite sides are equal to each other in a rectangle, we can state that:
Now we can calculate the perimeter of the rectangle by adding all sides together:
Answer
62
Exercise #13
Look at the triangle in the figure.
What is the length of the hypotenuse given that its perimeter is cm?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
We calculate the perimeter of the triangle:
As we want to find the hypotenuse (BC), we isolate it:
Then calculate AC using the Pythagorean theorem:
We then simplify the two:
We simplify to obtain:
Now we can replace AC with the value we found for BC:
Answer
cm