As we have already learned, Coordinate System has two axes and, therefore, any value defined by this coordinate system must include two values. These two values are called "ordered pairs".
Ordered Pairs Practice Problems and Solutions - Math Help
Master ordered pairs with step-by-step practice problems. Learn to identify coordinates, plot points, and solve function equations with detailed examples and solutions.
- Identify and write ordered pairs (X, Y) from coordinate graphs
- Calculate Y values from given X values in linear equations
- Plot ordered pairs accurately on coordinate planes
- Determine which ordered pairs belong to specific functions
- Solve for missing coordinates in ordered pair problems
- Apply ordered pairs to real-world coordinate system scenarios
Understanding Ordered Pair
What is an ordered pair?
An ordered pair is a pair of numbers that "belong" to a function.
An ordered pair is generally represented in parentheses where the value on the left within the parentheses represents the solution, while the value on the right within the parentheses represents the function value, that is, the result.
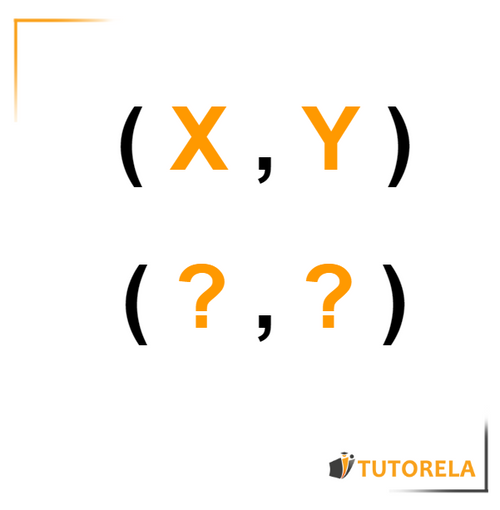
- When the function is represented by an equation, then is the value placed in the equation, while is the result obtained.
- When the function is represented through a graph, each point on the graph is essentially an ordered pair. That is, if we move vertically from the point to the axis (the axis runs from left to right), we obtain the value on the left within the parentheses. Conversely, if we move from the point vertically to the axis (the axis that goes from bottom to top), we obtain the correct value within the parentheses.
An ordered pair represents virtually all the points on the function graph
Practice Ordered Pair
Choose the appropriate drawing where the dots appear:
\( (6,6),\lparen-3,0) \)
Examples with solutions for Ordered Pair
Which point is marked on the map?
Answer:
Which point is marked on the graph?
Answer:
Choose the appropriate drawing where the dots appear:
Answer:
Choose the appropriate drawing where the dots appear:
Answer:
Choose the figure that shows the following points:
Answer: