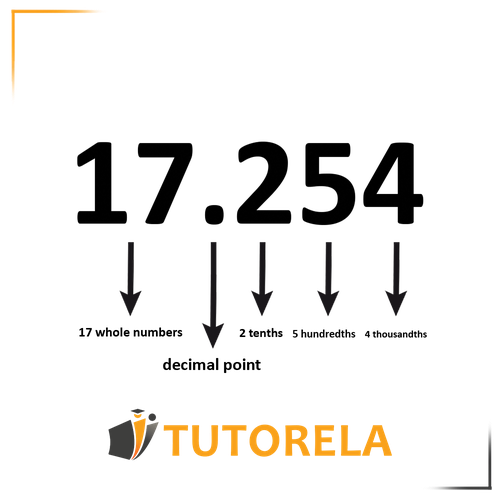
To convert a decimal fraction to a mixed fraction,
we ask ourselves how to read the decimal fraction or in other words, what the last digit represents –
if we use the word tenths – we place 10 in the denominator
if we use the word hundredths – we place 100 in the denominator
if we use the word thousandths – we place 1000 in the denominator
Converting Decimals to Mixed Numbers Practice Problems
Master converting decimal fractions to mixed numbers and simple fractions with step-by-step practice problems. Learn tenths, hundredths, and thousandths conversion techniques.
- Convert decimals like 9.56 to mixed numbers using place value understanding
- Identify tenths, hundredths, and thousandths in decimal fractions correctly
- Practice reading decimal fractions aloud to determine proper denominators
- Simplify converted fractions to lowest terms when possible
- Apply conversion skills to real-world decimal problems
- Build confidence with step-by-step conversion methods
Understanding Converting Decimal Fractions to Simple Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Converting a decimal to a mixed number
The number itself – everything that appears after the decimal point, we place in the numerator.
The whole number in the decimal fraction, we add to the mixed fraction as the whole number in the mixed fraction.
Practice Converting Decimal Fractions to Simple Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Write the following fraction as a decimal:
\( \frac{50}{100}= \)
Examples with solutions for Converting Decimal Fractions to Simple Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Write the following fraction as a decimal:
Let's write the simple fraction as a decimal fraction
Since the fraction divides by 100, we'll move the decimal point once to the left and get:
We'll add the zero before the decimal point and get:
Answer:
0.05
Write the following fraction as a decimal:
Let's write the simple fraction as a decimal fraction
Since the fraction divides by 100, we move the decimal point once to the left and get:
We'll add the zero before the decimal point and get:
Answer:
0.03
Write the following fraction as a decimal:
Let's write the simple fraction as a decimal fraction
Since the fraction divides by 100, we move the decimal point once to the left and get:
We'll add the zero before the decimal point and get:
Answer:
0.03
Write the following fraction as a decimal:
Let's write the simple fraction as a decimal fraction
Since the fraction divides by 100, we move the decimal point once to the left and get:
We'll add the zero before the decimal point and get:
Answer:
0.11
Write the following fraction as a decimal:
Let's write the simple fraction as a decimal fraction
Since the fraction divides by 100, we move the decimal point once to the left and get:
We'll add the zero before the decimal point and get:
Answer:
0.19