When we come to use the order of operations, we can encounter various special cases.
Sometimes, these cases will affect the order of operations, and in other cases we can use them to make the solution path easier for ourselves.
Special Cases Order of Operations Practice Problems
Master special cases with 0, 1, reciprocals, and fraction lines in order of operations. Practice problems with step-by-step solutions and examples.
- Apply multiplication and division rules with zero and one
- Identify and work with reciprocal numbers in expressions
- Handle fraction lines as implied parentheses in calculations
- Recognize when zero makes entire expressions equal zero
- Use reciprocal shortcuts to simplify complex problems
- Solve expressions with undefined division by zero cases
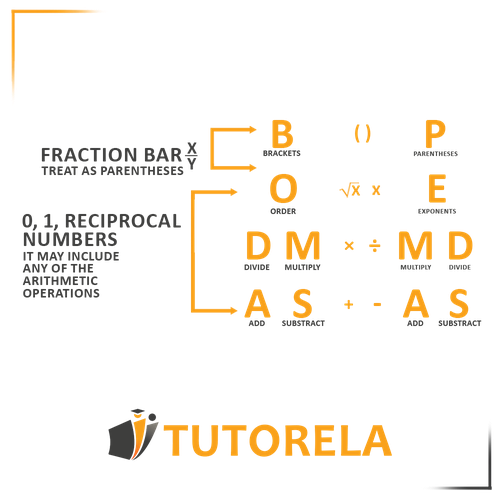
Understanding Special Cases (0 and 1, Inverse, Fraction Line)
Special Cases in Order of Operations
The number
Addition and subtraction do not affect the number.
Multiplication by =
Number divided by =
Division by is undefined
number
Multiplication by does not change the number
Division by does not change the number
Reciprocal Numbers
when is not equal to
Division and multiplication of reciprocal numbers
fraction line
Let's treat the arithmetic operation in the numerator as if the numerator is in parentheses.
Example
Solution:
Let's start by solving the numerator:
Let's continue with the parentheses:
Let's continue with multiplication and ignore adding :
Practice Special Cases (0 and 1, Inverse, Fraction Line)
Solve the following exercise:
\( 2+0:3= \)
Examples with solutions for Special Cases (0 and 1, Inverse, Fraction Line)
?
According to the order of operations, the exercise is solved from left to right as it contains only an addition operation:
Answer:
0.8
According to the order of operations, we first multiply and then add:
Answer:
12
?
According to the order of operations, the exercise is solved from left to right as it only involves an addition operation:
Answer:
13
First, calculate the expression within the parentheses:
Now, multiply the result by 9:
Thus, the final answer is 18.
Answer:
18
According to the order of operations, we first solve the expression in parentheses:
Now we multiply:
Answer:
40