The solution for an equation is a numerical value that, when inserted in the place of the unknown (or the variable), will render both members of the equation equal, that is, we will obtain a "true statement". In first degree equations with one unknown, there can only be one solution.
Example:
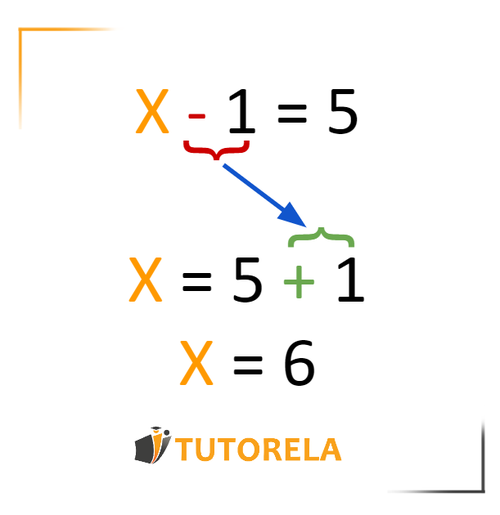
This is an equation with one unknown or variable indicated by the letter . The equation is composed of two members separated by the use of the equal sign . The left member is everything to the left of the sign , and the right member is everything to the right of the sign.
Our goal is to isolate the variable (or clear the variable) in order that it only remains in one of the members of the equation. In doing so we should be able to determine its value. In this article we will learn how to use the four mathematical operations(addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) to isolate the variable .