In order to calculate the sum of interior angles in a polygon, we will use the following formula:

In order to calculate the sum of interior angles in a polygon, we will use the following formula:

When-
= number of sides in a polygon
The formula can be applied to any polygon, whether it is convex, concave, or regular.
The sum of exterior angles in a polygon is degrees in any polygon, regardless of how many sides and angles it has.
First, let's recall what an exterior angle in a polygon is.
An exterior angle is an angle located between an original side and the extension of an original side - a side that extends outside the polygon.
The angle is located outside the polygon and therefore called - an exterior angle.
Let's observe this in the illustration:

In a regular polygon, all sides are equal and all interior angles are equal.
In order to determine the measure of an angle in a regular polygon, use the following formula:

When-
= number of sides in a polygon
Angles in a Regular Hexagon:
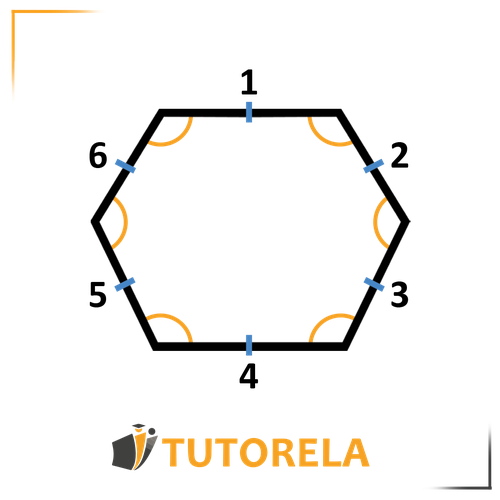
In every regular hexagon:
The sum of interior angles is
and the size of each angle will be
Let's proceed to a regular octagon:
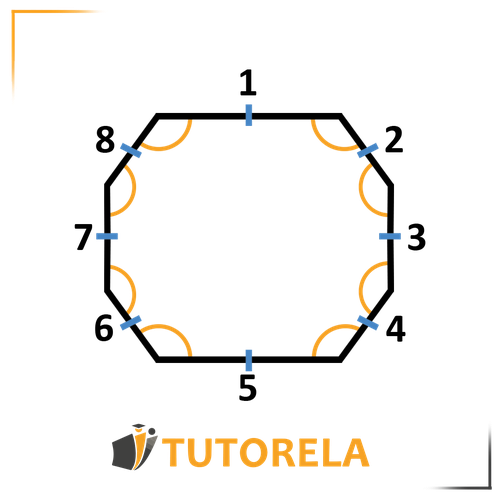
In every regular octagon:
The sum of interior angles is
and the size of each angle is degrees
In order to calculate the sum of interior angles in a polygon, we will use the following formula:

When-
= the number of sides in a polygon
The formula is applicable to any polygon, whether it is convex, concave, or regular.
Note - An interior angle is an angle located between 2 sides of the polygon and positioned inside the polygon.

Steps to determine the sum of the interior angles in a polygon:
Pay attention -
To begin with, we will perform the operation within the parentheses according to the order of operations. We will subtract 2 from the number of sides of the polygon and then proceed to multiply by .
The sum of exterior angles in a polygon is degrees in any polygon, regardless of how many sides and angles it has.
First, let's recall what an exterior angle in a polygon is.
An exterior angle is an angle located between an original side and the extension of an original side - a side that extends outside of the polygon.
The angle is located outside of the polygon and therefore called - an exterior angle.
Let's observe this in the illustration:

Observe the original sides of the polygon and imagine that whoever drew the polygon overdrew one of the sides.
The angle between the original side and the side which was overdrawn will be the exterior angle.
The sum of the exterior angles will always amount to degrees in any polygon you encounter.
Note - An angle between a leg and a leg is not considered an exterior angle.
For example:

In a regular polygon, all sides are equal and all interior angles are equal.
In order to determine the measure of an angle in a regular polygon, use the following formula:

When-
= number of sides in a polygon
Note-
The formula is similar to the formula for the sum of interior angles in a polygon.
What's added is the division by the number of sides of the regular polygon, which equals the number of angles in a regular polygon.
Steps for finding the angle measure of a weighted average:
Angles in a regular hexagon:

A regular hexagon is a polygon with six sides where all sides are equal and all angles are equal, rendering it a regular polygon.
Therefore, the formula for calculating the interior angle of a hexagon will be identical to the formula for the interior angle in a regular polygon:

Note - in every regular hexagon:
The sum of interior angles is
and the size of each angle will be
And now let's move on to a regular octagon:

A regular octagon is a polygon with eight sides where all sides are equal and all angles are equal.
Therefore, the formula for calculating the interior angle of a hexagon will be identical to the formula for the interior angle of a regular polygon:

We will proceed to calculate the sum of angles in a regular octagon -
We will use the formula to determine the sum of interior angles in a polygon:
And now we'll calculate the value of an angle in a regular octagon:
Since all angles are equal, we simply divided by the number of angles in a regular octagon.
Note - in every regular octagon:
The sum of interior angles is
and the size of each angle is degrees