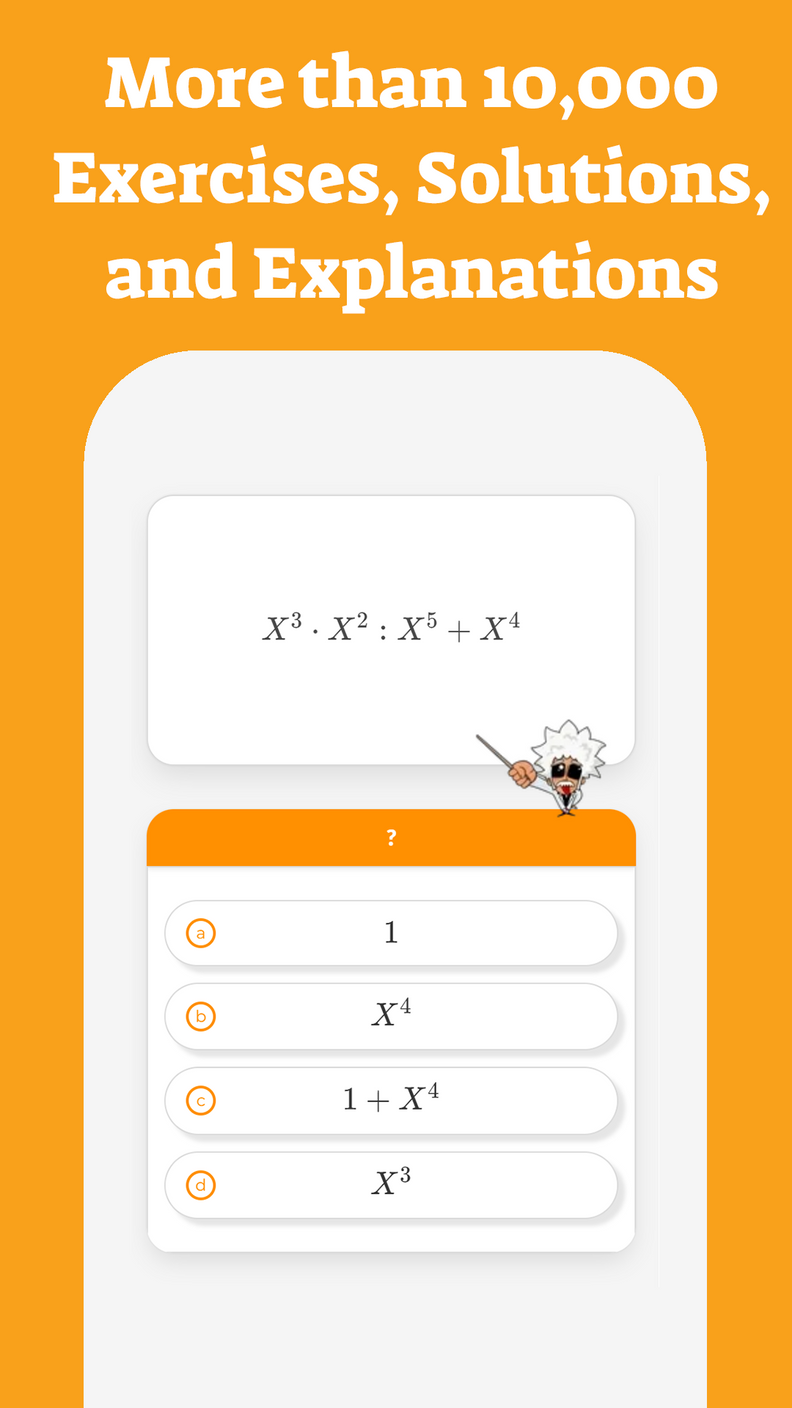
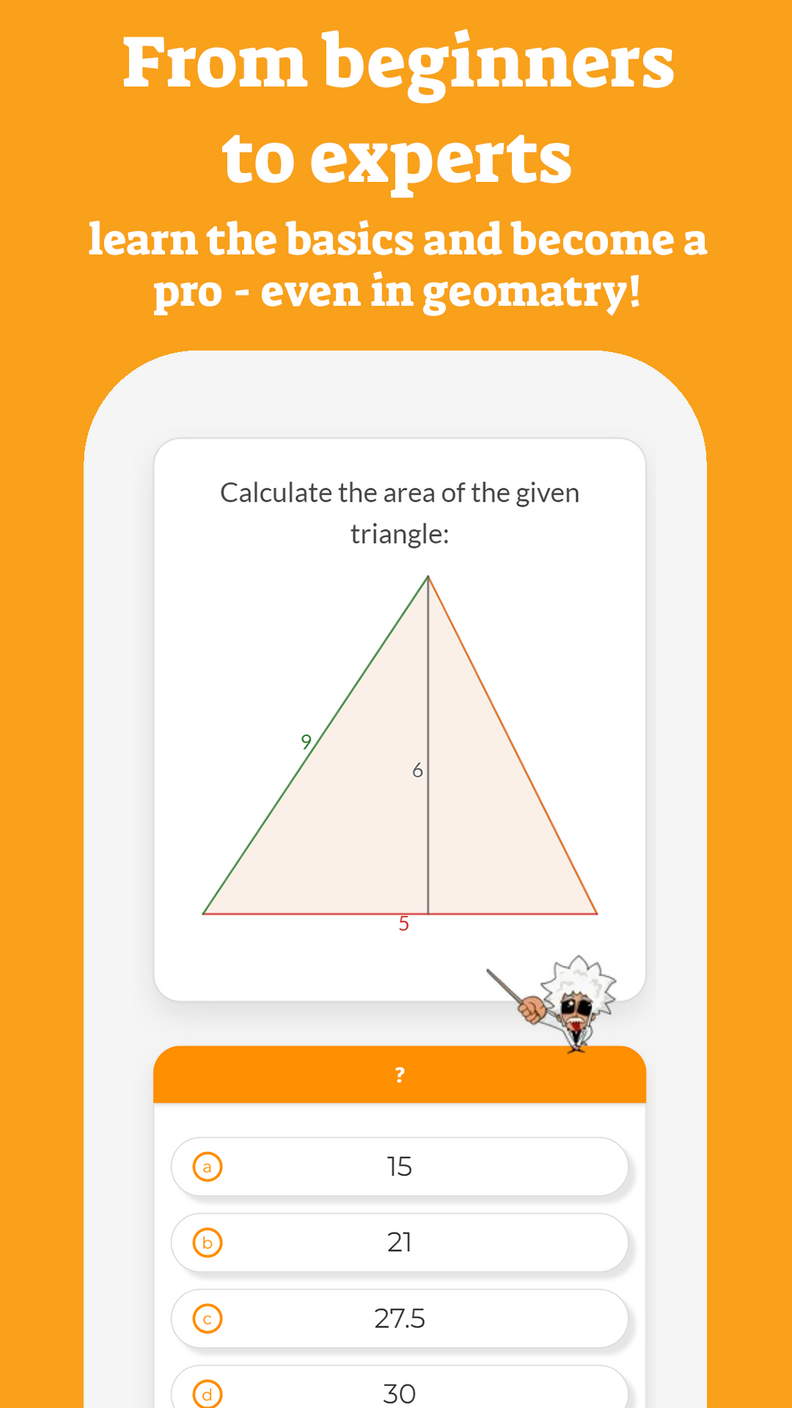
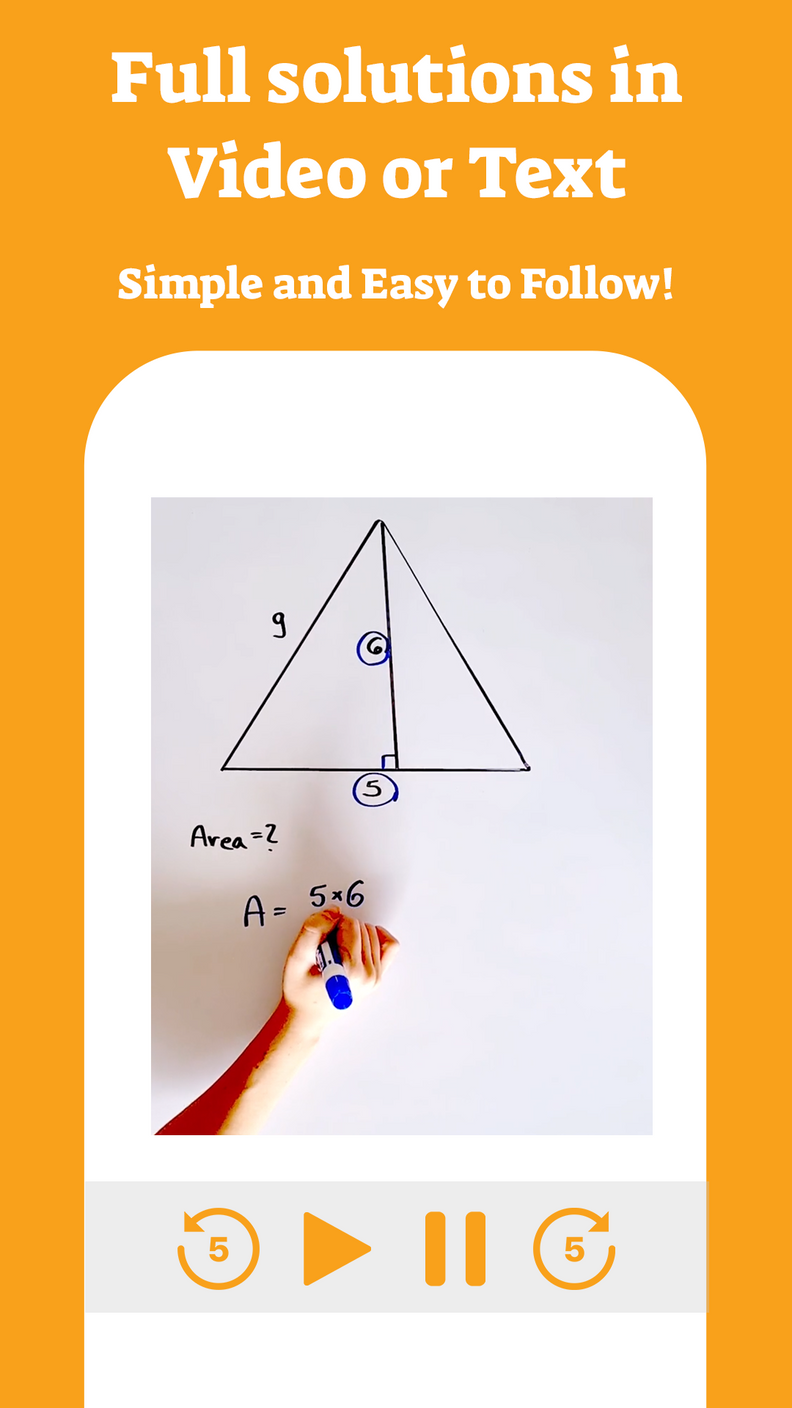
The trapezoid is considered one of the most intimidating shapes for students, therefore we have decided to provide a summary of the general idea behind the trapezoid and explain its properties to them and introduce some types of trapezoids.
Trapezoids
Characteristics of the Trapezoid
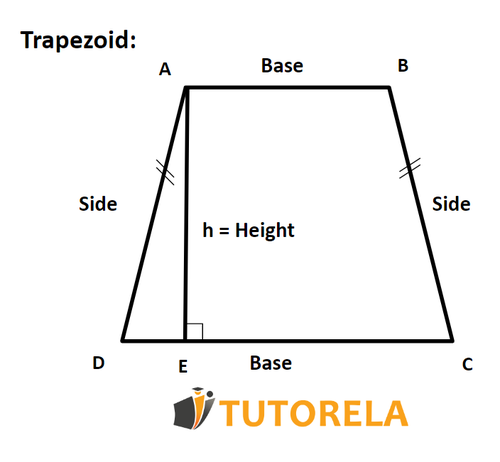
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral based on 4 sides like any other,
but special in that it will always have two parallel sides also called bases, which we can call the larger base and the smaller base
and it will also have two opposite sides also called legs.
Test yourself on trapezoid for ninth grade!
True OR False:
In all isosceles trapezoids the base Angles are equal.
Types of Trapezoids
There are several types of trapezoids that you will encounter during your studies.
For example, there are trapezoids where the lines look in the same direction and it is called a parallelogram
Additionally, there is a trapezoid that has two sides of the same length and it is called an Isosceles trapezoid. In the first example, we have a right angle trapezoid, which is a trapezoid where the height is equal to the side perpendicular to the bases so that 2 right angles are formed.
Exercises with Explanations on the Topic: Properties and Types of Trapezoids
Exercise 1
How do we calculate the area of a trapezoid?
We are given the following isosceles trapezoid with the following characteristics:
Task:
What is its height?
Solution:
Formula for the area of a trapezoid:
Substituting these values into our formula we have the following:
And we solve:
Answer:
Height is equal to .
Do isosceles trapezoids have two pairs of parallel sides?
Below is an isosceles trapezoid
If \( ∢D=50° \)
Determine the value of \( ∢B \)?
Given the following trapezoid:
Calculate the area of the trapezoid ABCD.
Exercise 2
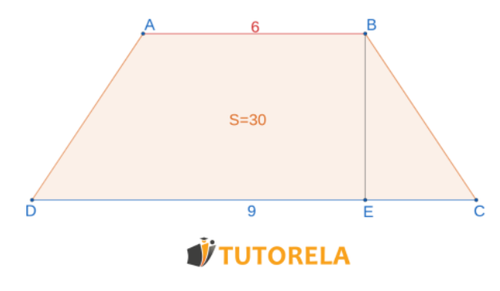
Given the area of a trapezoid where its lower base is twice the upper base and times greater than the height.
The area of the trapezoid is equal to (find help starting from )
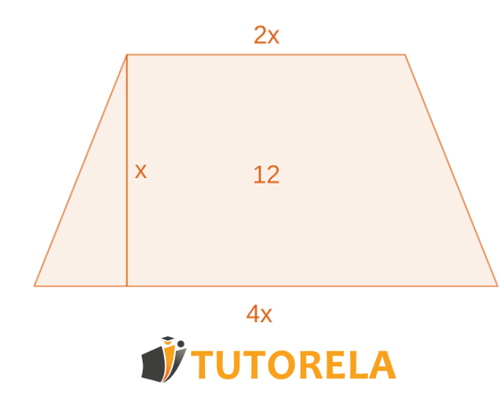
Task:
Calculate the value of .
Solution:
Given that the lower base is twice the upper base and times larger than the height.
if we divide everything by
Now taking the square root of both sides
Answer:
Exercise 3
Given that is an isosceles trapezoid with the following characteristics
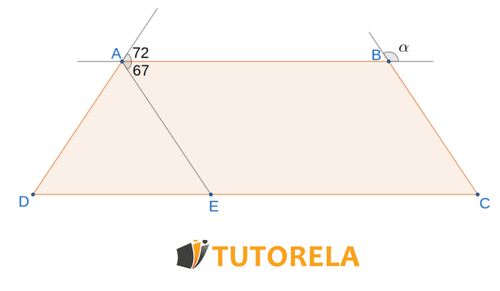
Task:
Find the angles of the trapezoid and the angle
Solution:
The sum of adjacent angles
This is because is an isosceles triangle
Opposite the equal sides of the triangle
The sum of the adjacent angles in the trapezoid are equal to
between the two bases
Angles opposite by the vertex
Answer:
Given the trapezoid:
What is the area?
Given the following trapezoid:
Calculate the area of the trapezoid ABCD.
Look at the trapezoid in the figure.
Calculate its perimeter.
Exercise 4
Given that is an isosceles trapezoid
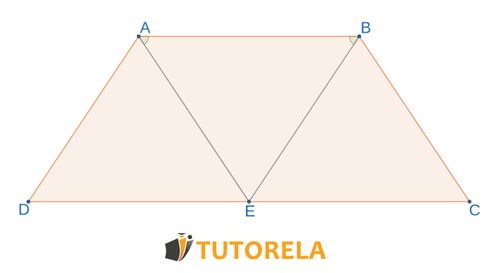
Task:
What is the midsegment opposite to in the triangle whose base is equal to?
Solution:
--->
Given the figure that:
The rule:
Opposite sides are equal in , is equal to the sides
Side =
Side =
Angle =
According to the side, side, angle congruence theorem
Corresponding sides between overlapping triangles
A midsegment in a triangle is equal to half of the side it corresponds to.
Midsegment =
Answer:
Exercise 5
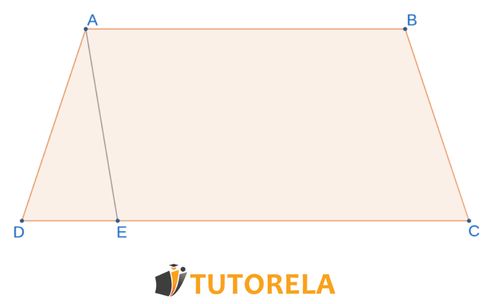
The area of the trapezoid
The line creates the triangle and the parallelogram .
It is known that the ratio of the area of the triangle to the area of the parallelogram is .
Task:
Calculate the ratio between the sides and .
Solution:
To calculate the ratio between the sides we will use the figure that:
We calculate using the formula to find half of the area and place the ratio.
To solve the equation, multiply across the factors.
Dividing everything by we have the following:
The ratio between is
Answer:
Answer:
What is the perimeter of the trapezoid in the figure?
The trapezoid ABCD is shown below.
AB = 2.5 cm
DC = 4 cm
Height (h) = 6 cm
Calculate the area of the trapezoid.
Given: \( ∢C=2x \)
\( ∢A=120° \)
isosceles trapezoid.
Find x.
Review Questions
What are the characteristics of trapezoids?
The characteristics of a trapezoid are those that help us define or classify which type of trapezoid we are referring to. It's important to remember that there are different types of trapezoids, such as the isosceles trapezoid, the right trapezoid, or a parallelogram. Therefore, it is very important to take into account the characteristics of each one.
What characteristics does a right trapezoid have?
The characteristics of a right trapezoid are that it has two right angles, one acute angle, and one obtuse angle, resulting in two of its sides being equal.
What are the elements of a trapezoid?
As we have already mentioned, a trapezoid is a quadrilateral (4 sides) that has two parallel sides, which are called bases, usually considered as the larger base and the smaller base, it has a height, and it has 4 angles.
What is an isosceles trapezoid?
An isosceles trapezoid is one that has two equal sides, which are the sides that join its parallel lines. This is one of the main characteristics of this type of trapezoid.
Given the trapezoid:
What is its perimeter?
Given the following trapezoid:
Calculate the area of the trapezoid ABCD.
What is the area of the trapezoid ABCD?
Examples with solutions for Trapezoids
Exercise #1
True OR False:
In all isosceles trapezoids the base Angles are equal.
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
True: in every isosceles trapezoid the base angles are equal to each other.
Answer
True
Exercise #2
Do isosceles trapezoids have two pairs of parallel sides?
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve this problem, we'll follow these steps:
- Step 1: Define the geometric properties of a trapezoid.
- Step 2: Define the geometric properties of an isosceles trapezoid.
- Step 3: Conclude whether an isosceles trapezoid has two pairs of parallel sides based on these definitions.
Now, let's work through each step:
Step 1: A trapezoid is defined as a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides.
Step 2: An isosceles trapezoid is a special type of trapezoid where the non-parallel sides (legs) are of equal length. Its defining feature is having exactly one pair of parallel sides, which is the same characteristic as a general trapezoid.
Step 3: Since the definition of a trapezoid inherently allows for only one pair of parallel sides, an isosceles trapezoid, as a type of trapezoid, cannot have two pairs of parallel sides. A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides is typically designated as a parallelogram, not a trapezoid.
Therefore, the solution to the problem is that isosceles trapezoids do not have two pairs of parallel sides. No.
Answer
No
Exercise #3
Below is an isosceles trapezoid
If
Determine the value of ?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
Let's recall that in an isosceles trapezoid, the sum of the two angles on each of the trapezoid's legs equals 180 degrees.
In other words:
Since angle D is known to us, we can calculate:
Answer
130°
Exercise #4
Given the following trapezoid:
Calculate the area of the trapezoid ABCD.
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve this problem, we follow these steps:
- Step 1: Identify the given dimensions of the trapezoid.
- Step 2: Use the formula for the area of a trapezoid.
- Step 3: Substitute the given values into the formula and calculate the area.
Now, let's work through these steps:
Step 1: We know from the problem that trapezoid ABCD has bases and , with a height of .
Step 2: The formula for the area of a trapezoid is:
Step 3: Plugging in the values:
Therefore, the area of the trapezoid ABCD is .
Answer
26
Exercise #5
Given the trapezoid:
What is the area?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
Formula for the area of a trapezoid:
We substitute the data into the formula and solve:
Answer
52.5
More Questions
Area of a Trapezoid
- Solve for X: Trapezoid with Area 60 and Bases 8 and 14
- Calculate Trapezoid Height X: Area 30 with Bases 3.5 and 7.5
- Calculate X in Trapezoid: Given Height 5 and Base 7
- Calculate Trapezoid Area: Finding Space Between 9.6 and 13 Units
- Calculate Trapezoid Area: Finding Space with 5-Unit Top Base and 6-Unit Height
Trapeze
- Calculate Trapezoid Height: Given Area 30 and Parallel Sides 6 and 9
- Calculate the Area of an Equilateral Hexagon with Side Length 7 and Height 12.124
- Calculate Trapezoid Area: Isosceles Triangle with Height 8 and Base 17
- Calculate Trapezoid Perimeter: Inside an Isosceles Triangle with Height 8
- Trapezoid Area Calculation: Verifying and Applying the Formula with 4cm and 7cm Parallel Sides
Isosceles Trapezoids
- Isosceles Trapezoid Problem: Finding Angle B When B=3x and D=x
- Find Angle B = 2y+20 in an Isosceles Trapezoid with 60° Angle
- Isosceles Trapezoid Angle Property: Do Opposite Angles Always Sum to 180 Degrees?
- Isosceles Trapezoid Diagonals: Do They Have Equal Length and Intersect?
- Trapezoid Diagonal Intersection: Do Diagonals Always Bisect Each Other?
- Area
- Trapezoids
- Symmetry in Trapezoids
- Diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid
- Area of a trapezoid
- Perimeter of a trapezoid
- Types of Trapezoids
- Isosceles Trapezoid
- Parallelogram
- The area of a parallelogram: what is it and how is it calculated?
- Perimeter of a Parallelogram
- Identifying a Parallelogram
- Rotational Symmetry in Parallelograms
- From the Quadrilateral to the Parallelogram
- Kite
- Area of a Deltoid (Kite)
- Rectangle
- From a Quadrilateral to a Rectangle
- From a Parallelogram to a Rectangle
- Calculating the Area of a Rectangle
- The perimeter of the rectangle
- Congruent Rectangles
- The sides or edges of a triangle
- Triangle Height
- Midsegment
- Midsegment of a triangle
- Midsegment of a trapezoid
- The Sum of the Interior Angles of a Triangle
- Exterior angles of a triangle
- Square
- Area of a square
- From Parallelogram to Square
- Rhombus, kite, or diamond?
- Diagonals of a Rhombus
- Lines of Symmetry in a Rhombus
- From Parallelogram to Rhombus
- The Area of a Rhombus
- Perimeter
- Triangle
- Types of Triangles
- Obtuse Triangle
- Equilateral triangle
- Identification of an Isosceles Triangle
- Scalene triangle
- Acute triangle
- Isosceles triangle
- The Area of a Triangle
- Area of a right triangle
- Area of Isosceles Triangles
- Area of a Scalene Triangle
- Area of Equilateral Triangles
- Perimeter of a triangle
- Areas of Polygons for 7th Grade
- Right Triangle
- Area of a right-angled trapezoid
- Area of an isosceles trapezoid
- Median in a triangle
- Center of a Triangle - The Centroid - The Intersection Point of Medians
- How do we calculate the area of complex shapes?
- How to calculate the area of a triangle using trigonometry?
- How do we calculate the perimeter of polygons?
- All terms in triangle calculation
- Diagonals in a rectangle
- Symmetry in a kite