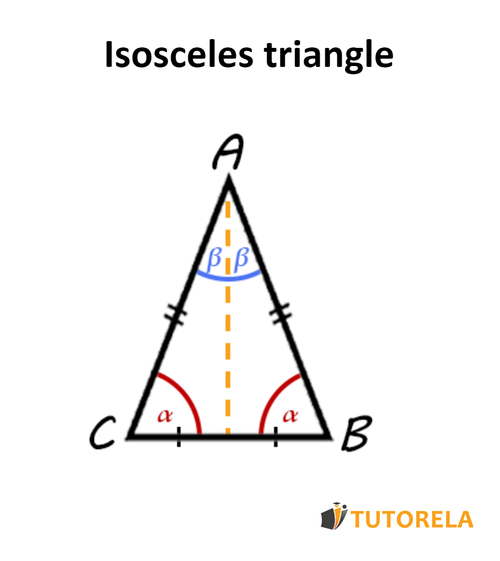
The isosceles triangle is a type of triangle that has two sides (legs) of equal length.
A consequence of having two sides of equal length implies that also the two angles opposite these sides measure the same.
Key Parts:
- Legs: The two equal sides
- Base: The third side (different length)
- Vertex angle: The angle between the two legs
- Base angles: The two equal angles adjacent to the base
This fundamental property—that equal sides create equal opposite angles—makes isosceles triangles essential building blocks in geometry and forms the basis for the Isosceles Triangle Theorem.