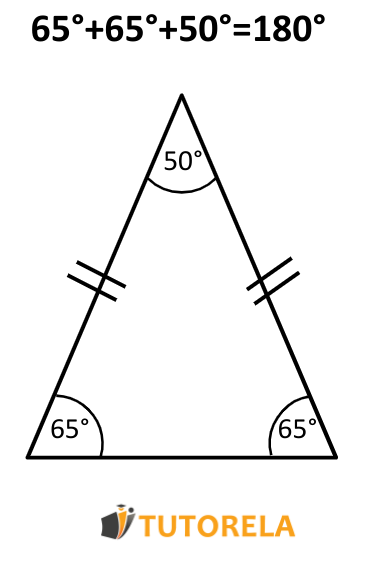
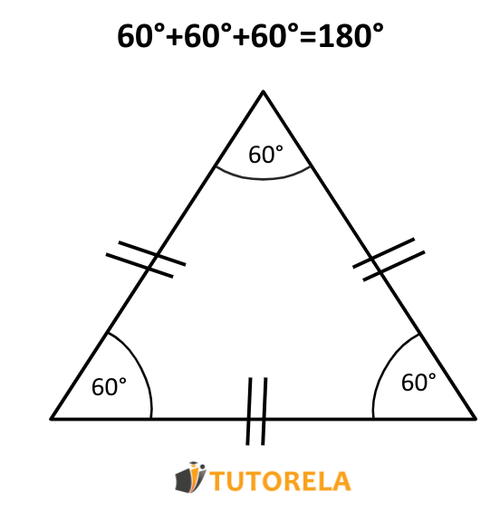
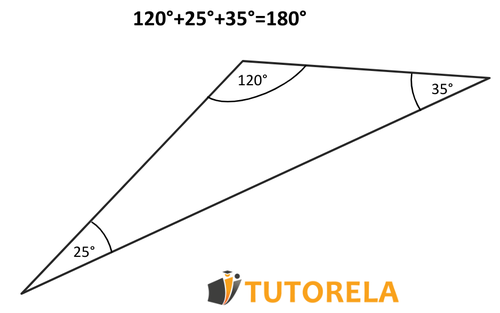
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is . If we add the three angles of any triangle we choose, the result will always be . This means that if we know the values of two angles of a triangle we can always calculate, with ease, the value of the third one: first we add the two angles we know and then we subtract from The result of this subtraction will give us the value of the third angle of the triangle.
For example, given a triangle with two known interior angles of and degrees, we are asked to discover the measure of the third angle. First we add plus resulting in degrees. Now we subtract from , yielding degrees. In other words, the third angle of the triangle equals degrees.
The above property is also called the triangle sum theorem, and can help us to solve problems involving the interior angles of a triangle, regardless of whether it is equilateral, isosceles or scalene.