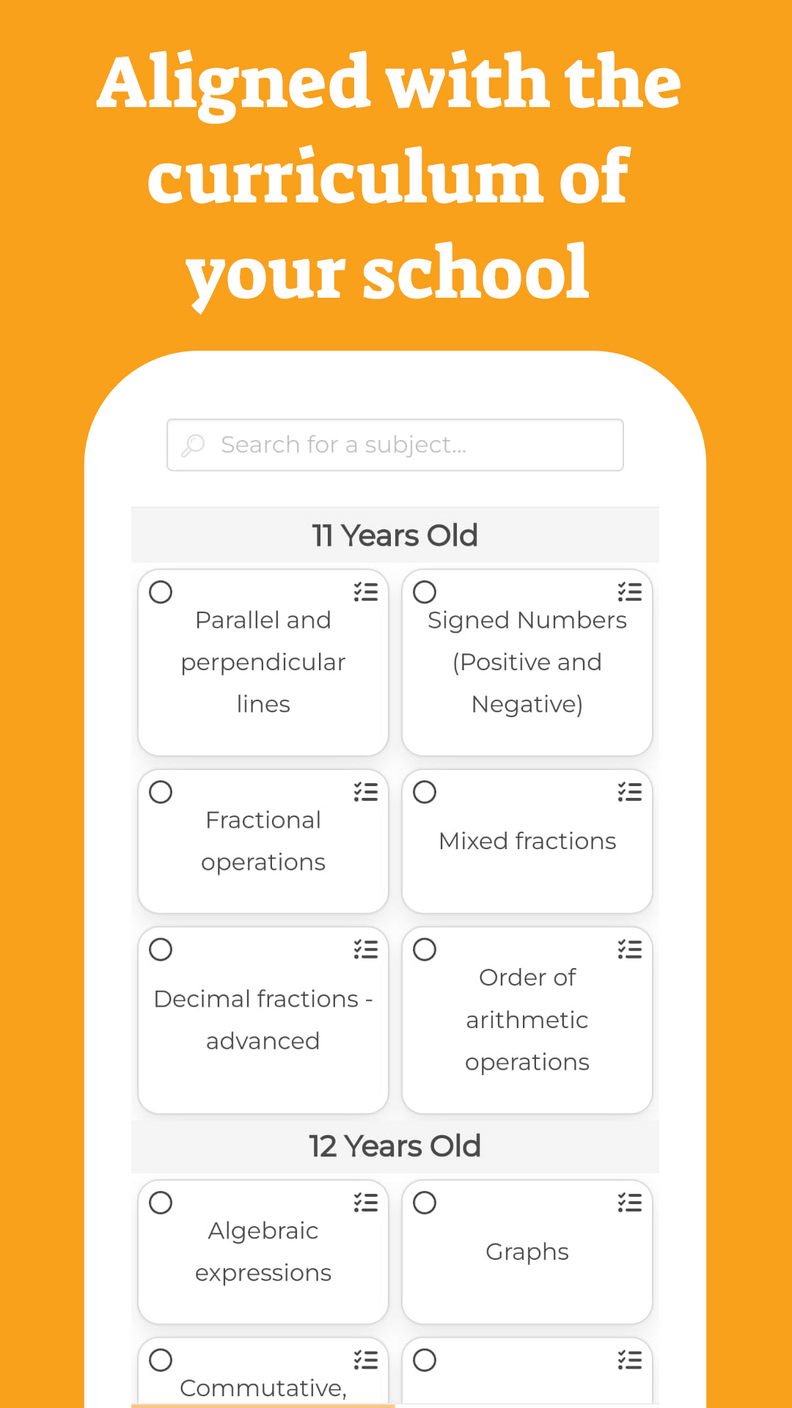
Constant Rate of Change
The meaning of the constant rate of change of a function can be seen when the variables change in fixed proportions and the do as well.
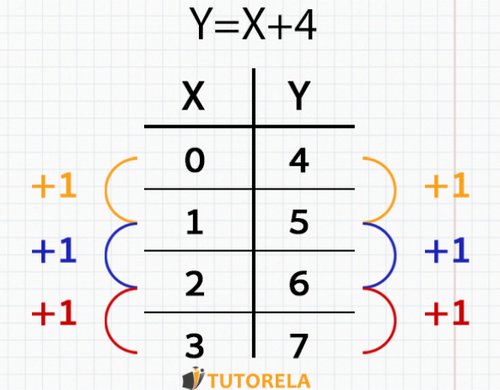
For example, if the constant interval of the is and also that of the is stable and does not vary from time to time.
The interval of the variables does not necessarily have to be equal to that of the for it to be considered a case of constant rate of change.
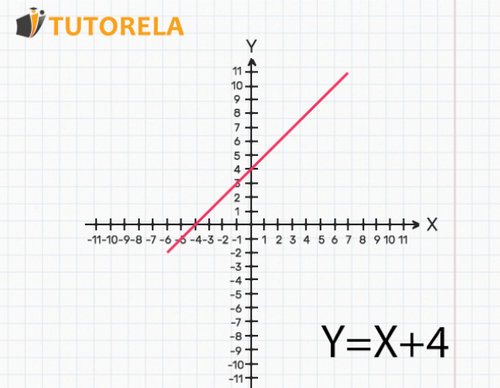
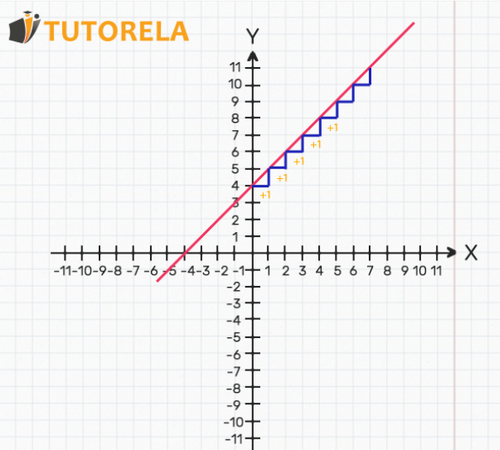
If the function is represented with a straight graph, it means that the rate of change is constant.
The rate of change is the slope of the function.
A constant rate of change is represented by a straight line, as seen in the following scheme: