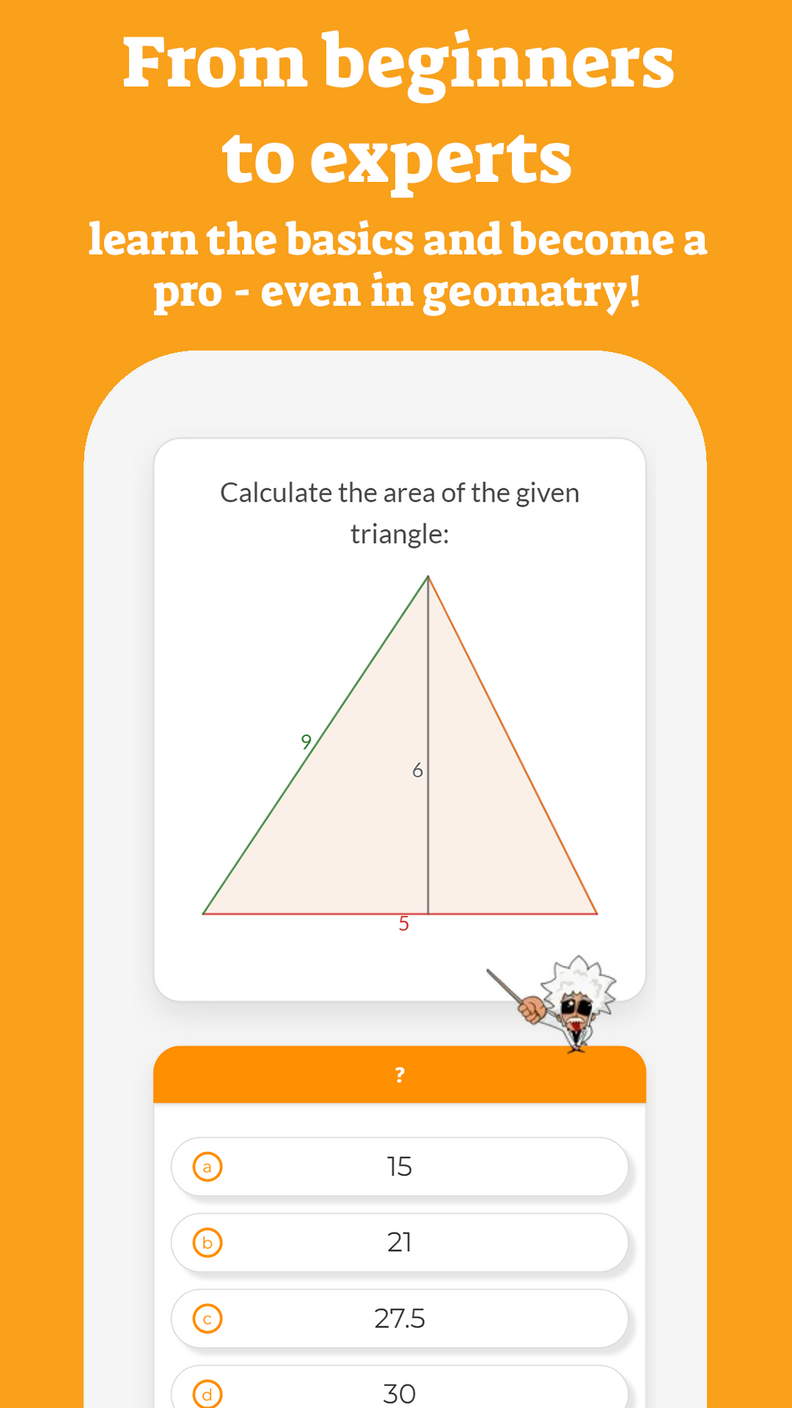
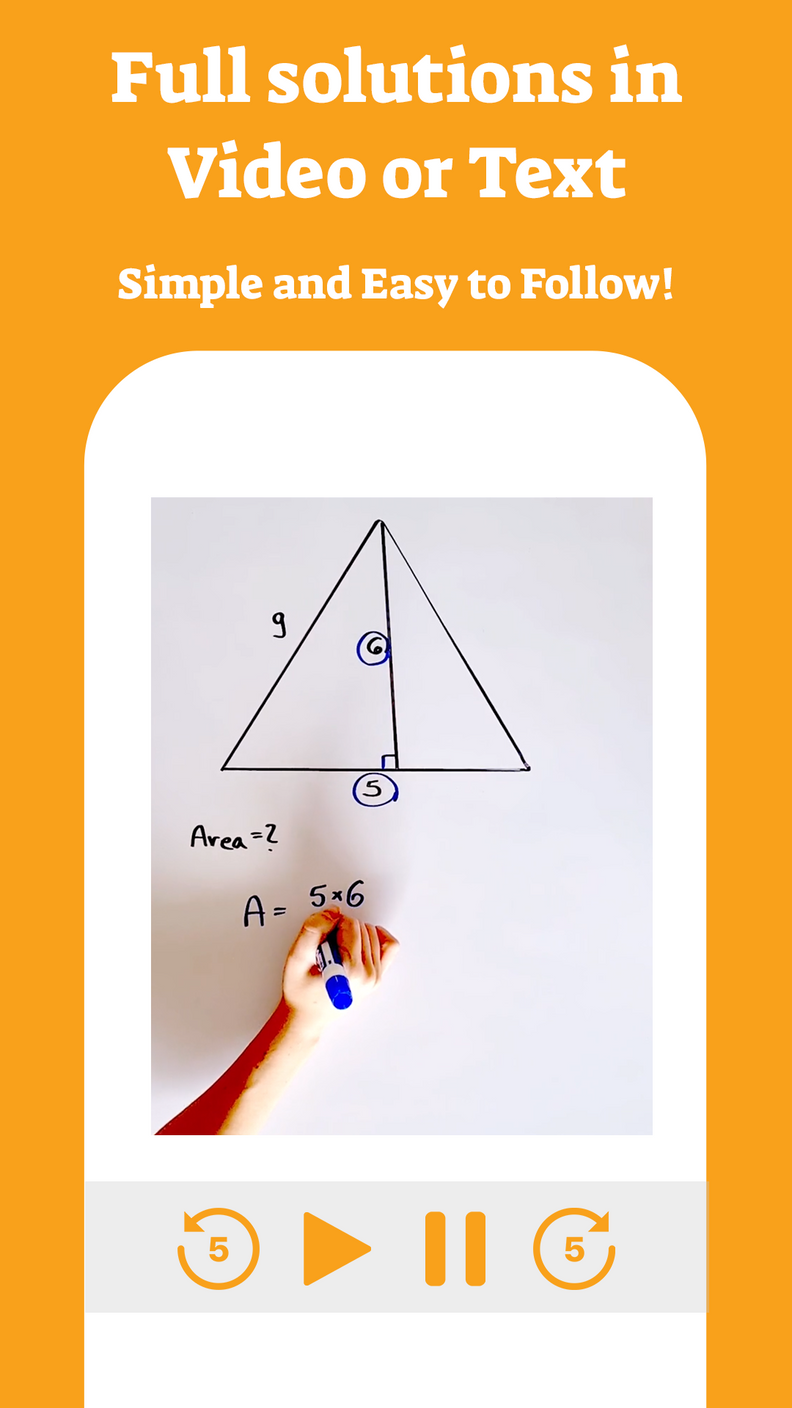
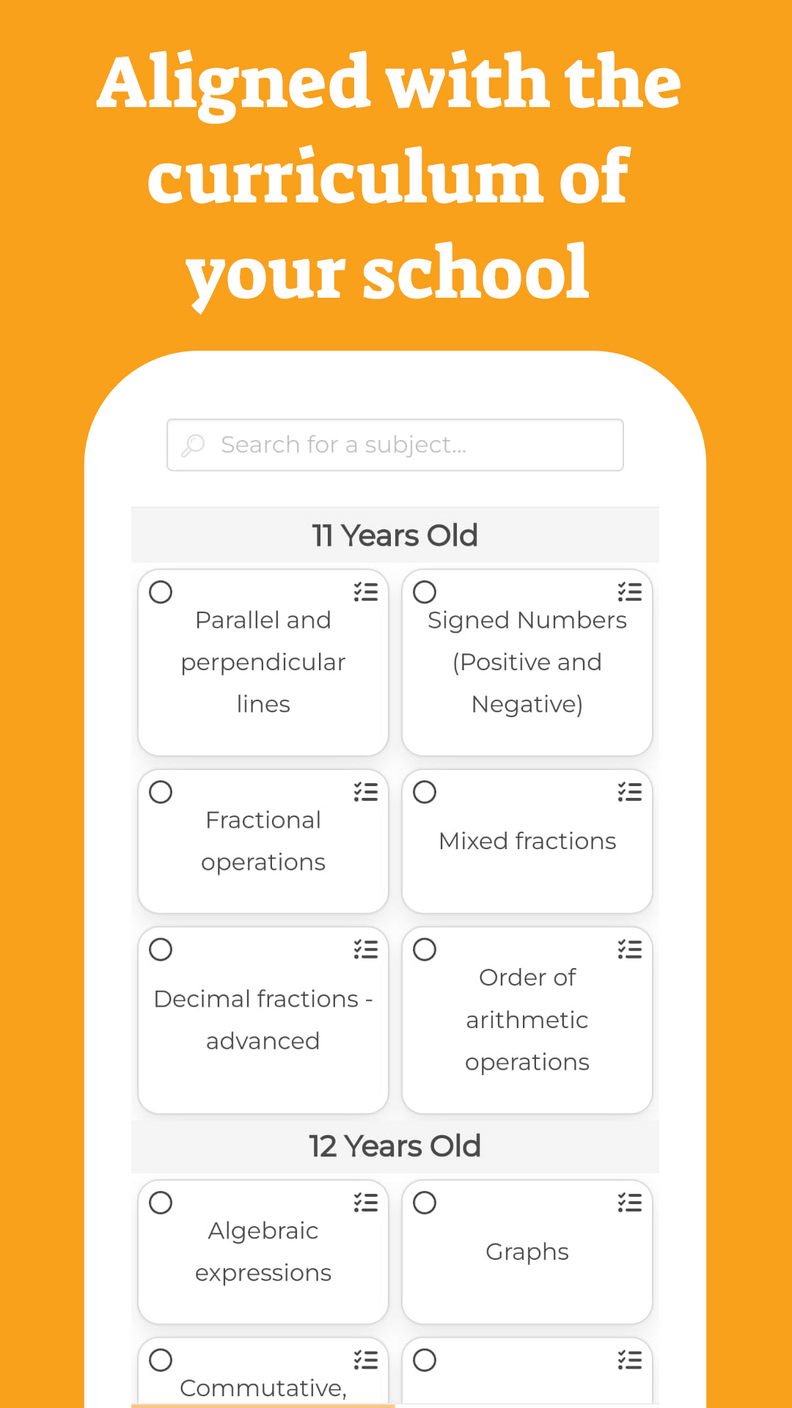
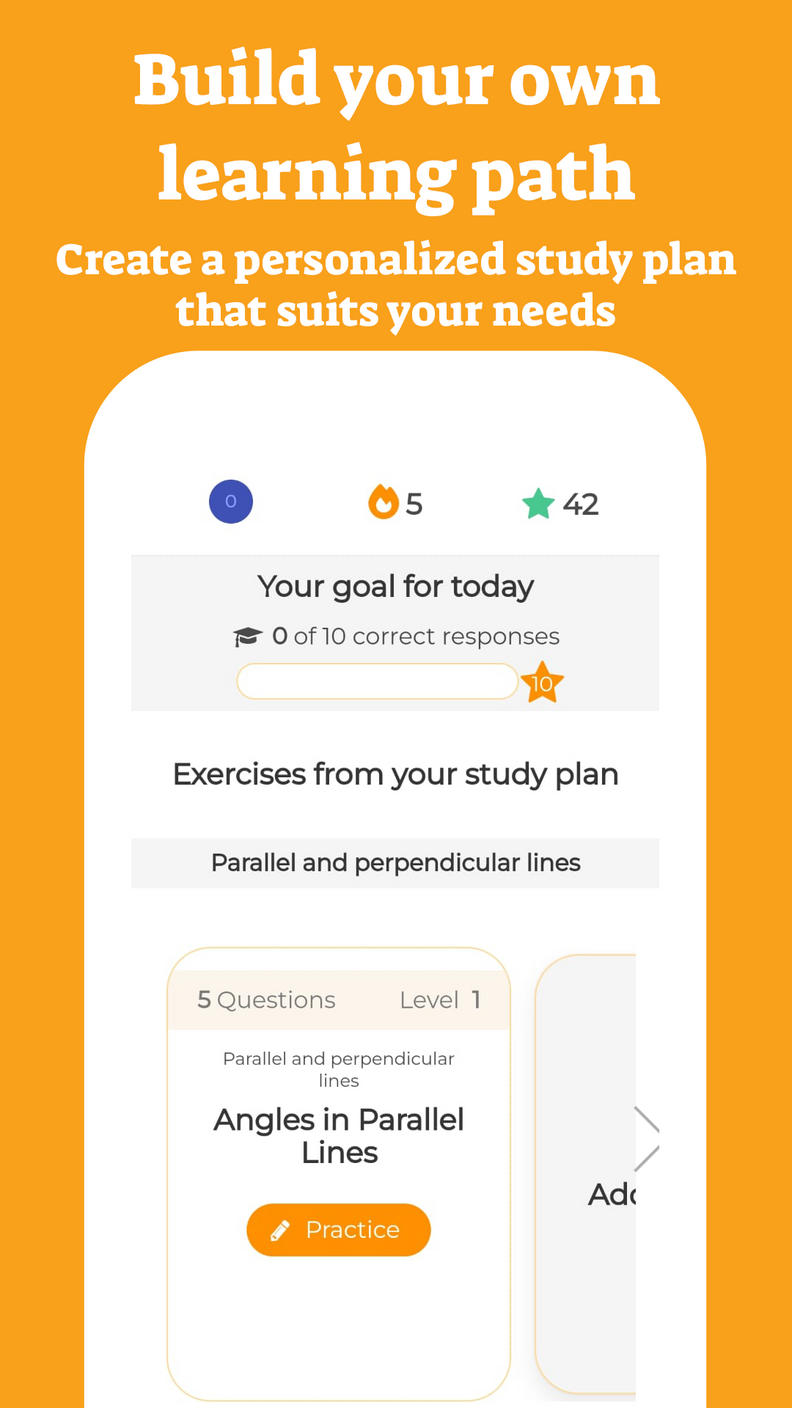
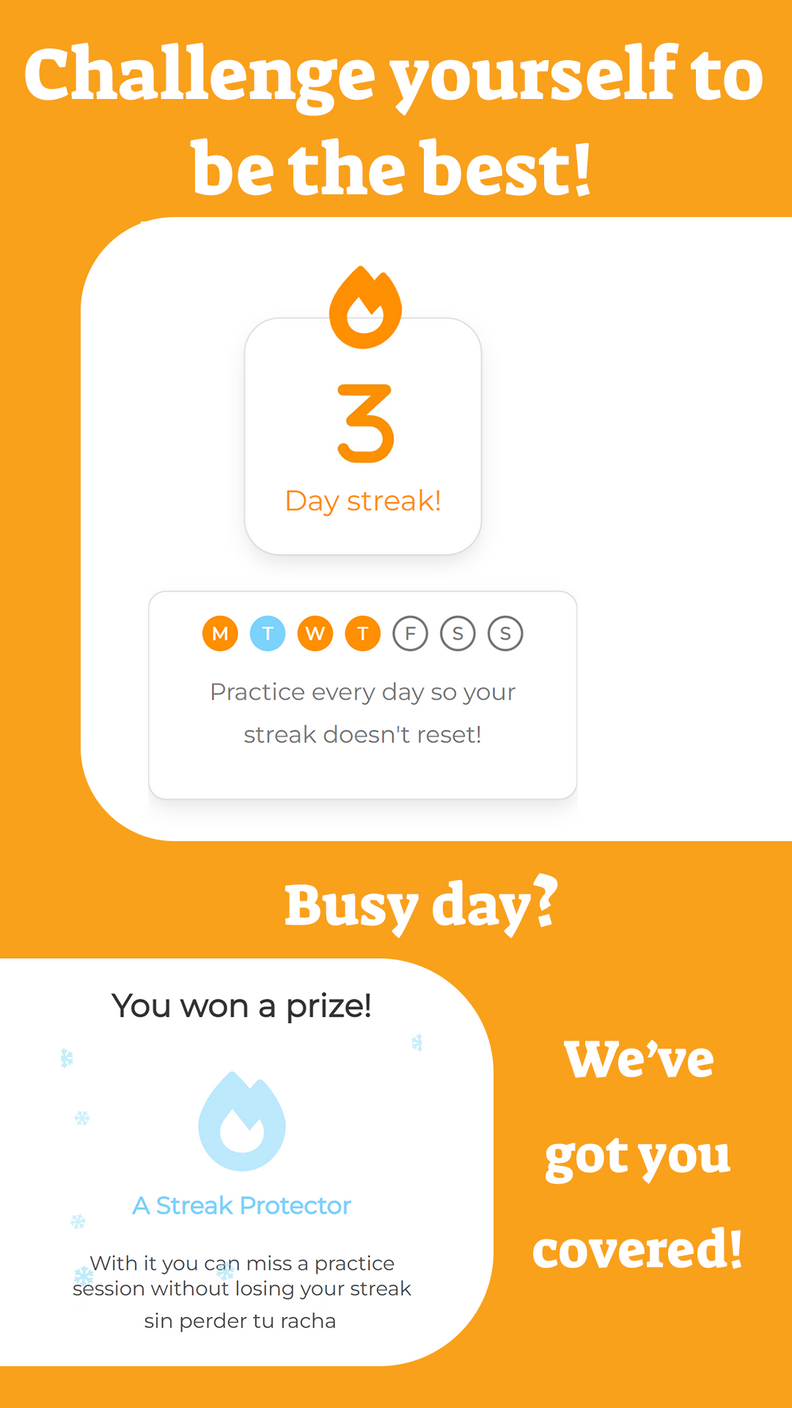
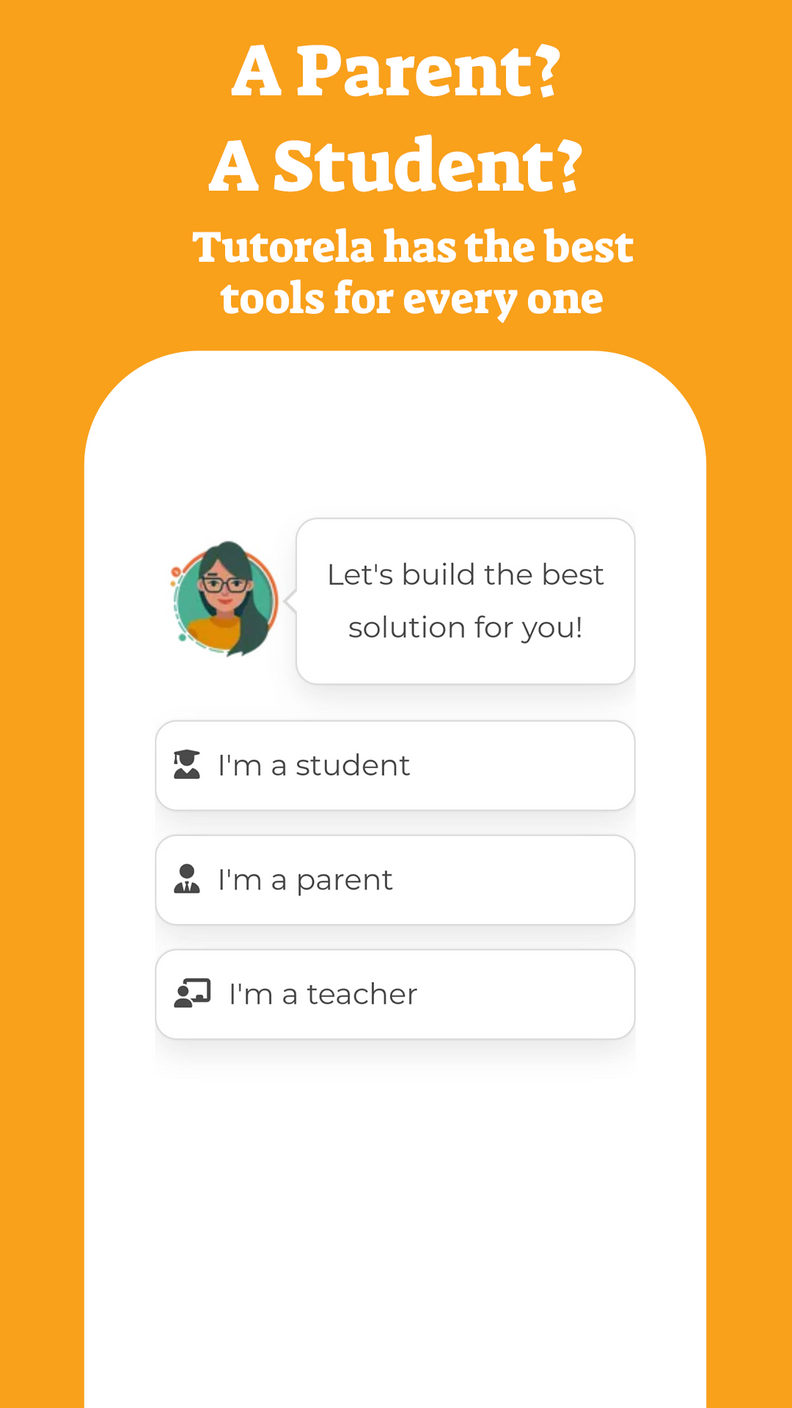
An integral can be defined for all values (that is, for all ). An example of this type of function is the polynomial - which we will study in the coming years.
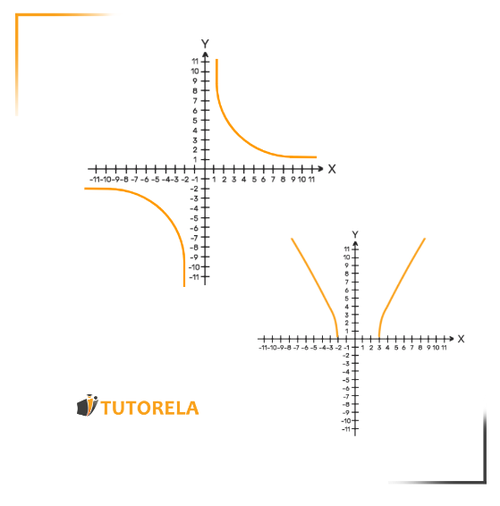
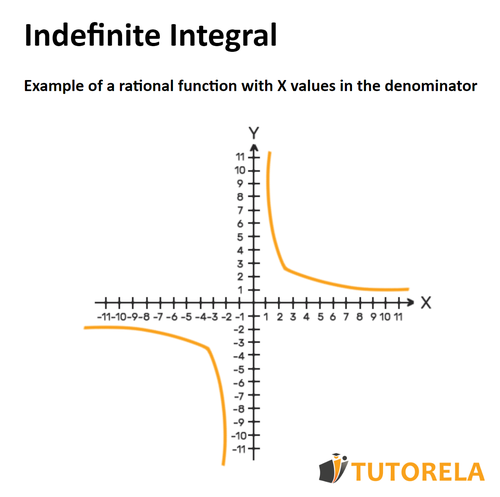
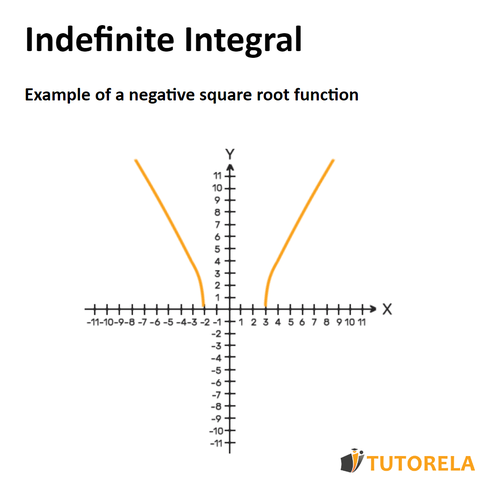
However, there are integrals that are not defined for all values (all ), since if we place certain or a certain range of values of we will receive an expression considered "invalid" in mathematics. The values of for which integration is undefined cause the discontinuity of a function.