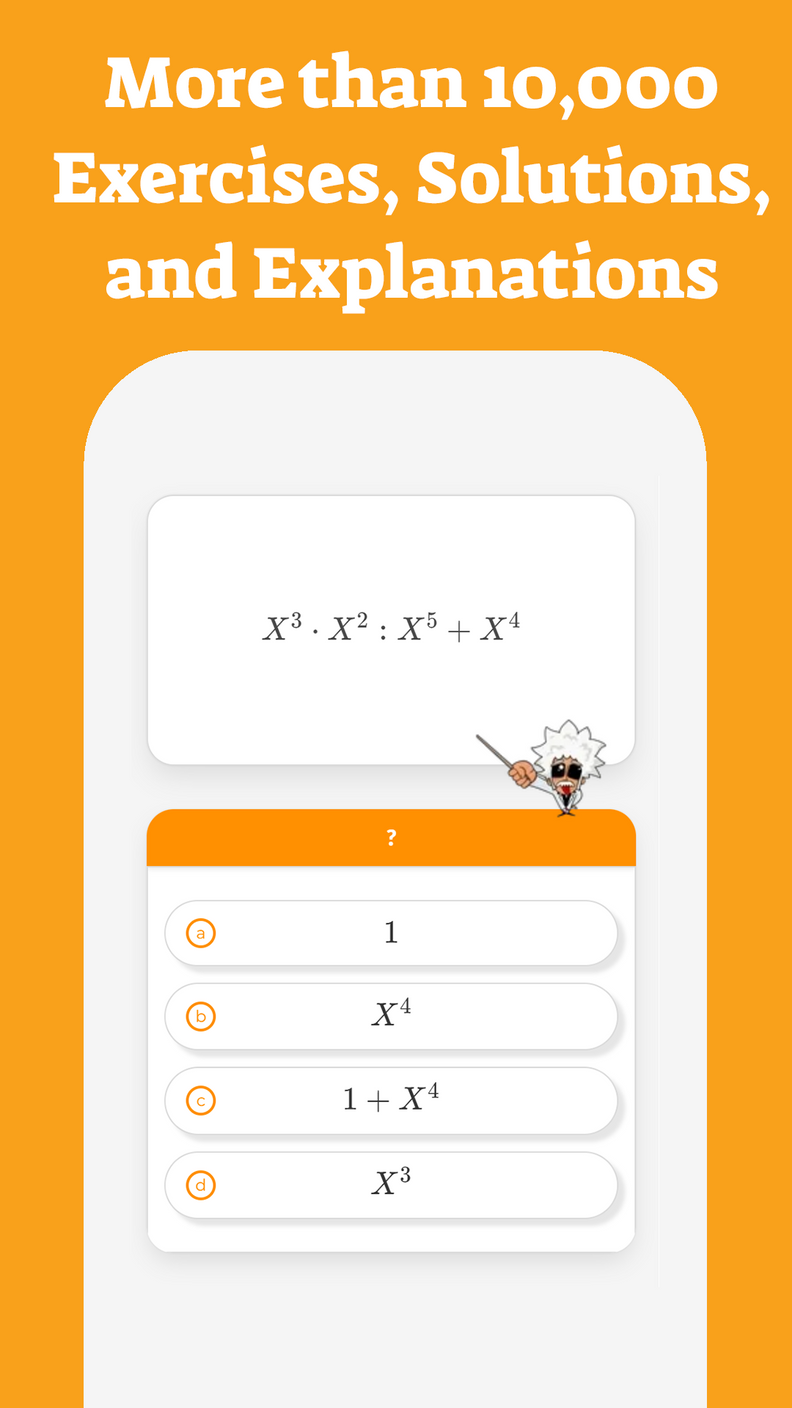
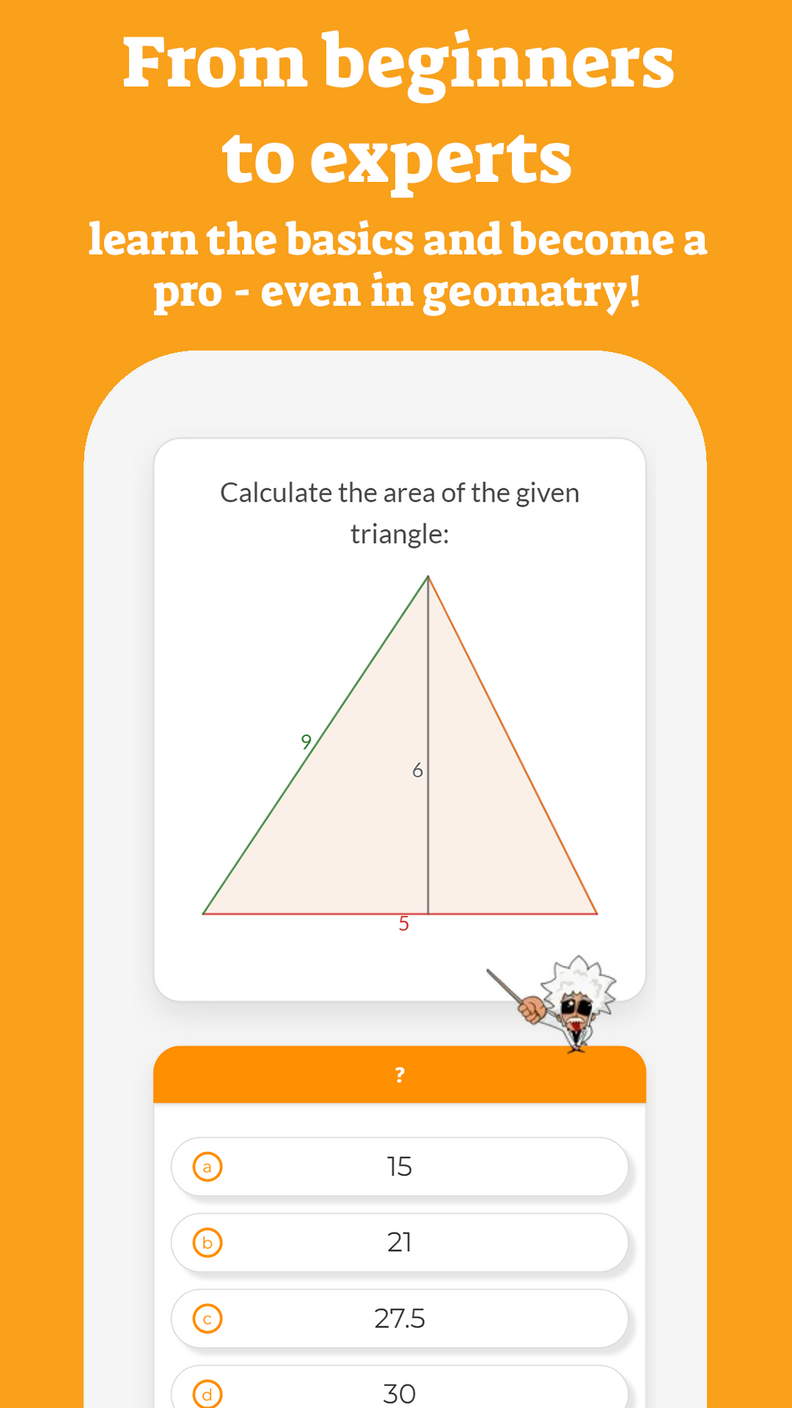
Inputing Values into a Function
In mathematics, we often assign numerical values to variables in equations or mathematical expressions. A function can be thought of as a machine: you input a value (called the input), the function processes it according to a specific rule, and produces a result (called the output). The input is usually represented by \(x)\, and the output by or .
Understanding Variables and Substitution
A variable is a placeholder for an unknown number, often called the "unknown". When we replace a variable with a specific value, we refer to this process as substitution.
- If an equation contains only one variable, we can solve for its value by isolating it.
- If an equation contains multiple variables, there can be multiple solutions. Each value substituted affects the remaining variables in the equation.
When we talk about inputting values into a function, we are essentially substituting the variables in a mathematical expression or equation with specific numerical values to evaluate the result.
Often "solving an equation" is actually finding the values of the variables inside it.
For example
Suppose we have three variables, two of which have known values:
We are also given the equation:
Remember! when facing this kind of questions, you want to try and find the values of the variables.
To solve the problem, we will first substitute the known values into the equation:
Simplify and solve:
By substituting the known values and performing the necessary operations, we were able to isolate and calculate the value of
Answer: