The area of the kite can be calculated by multiplying the lengths of the diagonals and dividing this product by .
Area of a Deltoid (Kite)
How do we calculate the area of a kite?
Deltoid Area Formula
To facilitate the understanding of the concept of calculus, you can use the following drawing and the accompanying formula:
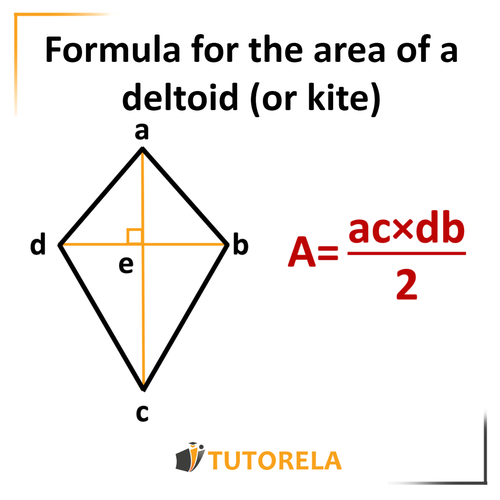
Test yourself on area of a deltoid!
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
There are many geometric shapes that can be found during the solving of engineering problems at all different stages of study, such as in high school, in matriculation exams, and even in psychometry. One of the less trivial shapes is the deltoid and, as part of the questions surrounding it, students are often asked to calculate the area of the deltoid.
What is the deltoid?
A deltoid is a polygon with four sides (that is, a quadrilateral) with two distinct sets of adjacent sides of equal length to each other.
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Types of Deltoids
There is a clear distinction between convex deltoid and concave deltoid.
Convex deltoid
Convex deltoid is a deltoid where the diagonals are inside and cross each other. The longer diagonal acts as a main diagonal, while the shorter diagonal acts as a secondary diagonal.
As you can observe in the following drawing, the main diagonal divides the deltoid into two overlapping triangles, that is, identical, and the secondary diagonal divides the deltoid into two isosceles triangles whose bases are adjacent and, indeed, identical.
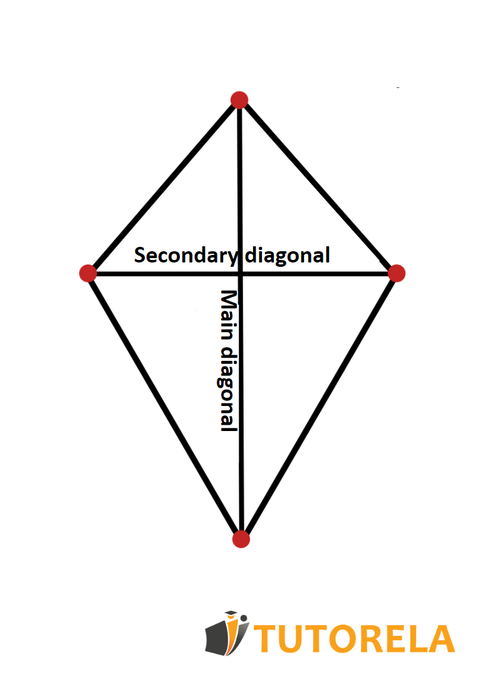
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Concave Kite
Concave kite is a kite where one of the diagonals (main diagonal) passes inside the kite and the other diagonal (secondary diagonal) passes outside the kite.
The concave deltoid can be described as a shape consisting of two isosceles triangles that share a common base, where one triangle contains the other triangle. The following drawing better describes the concave deltoid:
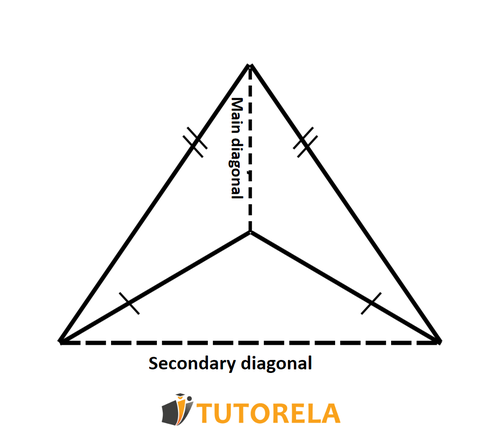
- When all sides of the kite have the same length, a rhombus is obtained, which is actually a special case of a kite.
- Another special case of a kite is a square, when it is a case where all sides and all angles are of the same size.
Properties of the Kite
- The angles on the sides, or more precisely, the angles between the different adjacent sides of the kite, are of equal size.
- The diagonals of the kite are perpendicular to each other
- The main diagonal in the convex kite (or its extension in the concave kite) crosses the secondary diagonal (in both cases), and therefore actually functions as a perpendicular bisector
- The main diagonal equally divides (crosses) the main angles of the kite
- Every convex kite has the possibility of enclosing a circle
- In every kite, there are two sets of adjacent sides of equal size
- As mentioned, a concave kite is characterized by a secondary diagonal located outside of it
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Practice on the Area of a Kite
Exercise 1
Given the kite whose area is cm², the meeting point of the diagonals and .
The area of the section KP must be calculated according to the attached drawing and the existing data:
- cm
- cm²
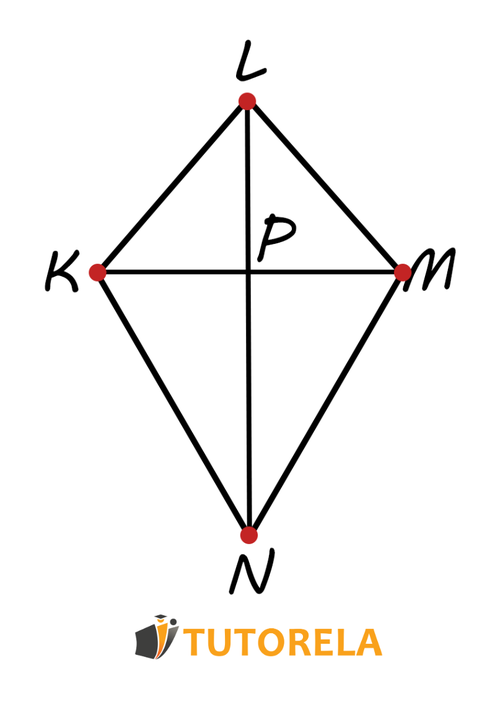
Solution:
This exercise is a reverse calculation, that is, we know the area and we are asked to calculate the length of the segment .
In the first step, we replace the data we know in the kite area formula.
We obtain:
We simplify the expression and obtain:
In fact, we found the length of the second diagonal of the kite.
According to one of the properties of the kite, the diagonal divides the diagonal into two equal parts.
From here we obtain that is equal to cm.
Answer:
cm
Examples and exercises with solutions for the Area of the Kite
Exercise #1
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
Initially, let us examine the basic properties of a deltoid (or kite):
A quadrilateral is classified as a deltoid if:
- It has two distinct pairs of adjacent sides that are equal in length.
In the question's image, we observe the following:
- There are lines connecting A to B, B to C, C to D, and D to A, suggesting a typical quadrilateral.
- The shape, given its central symmetry (as it is formed by joining these particular points which extend equal lines), is reminiscent of a symmetric or bilaterally mirrored formation.
- Given the symmetry, it suggests all internal angles are less than 180 degrees, confirming the figure as a convex shape.
From this analysis, the quadrilateral satisfies the characteristic of having pairs of equal adjacent sides which confirms it as a deltoid. The symmetry suggests it is not concave (which occurs when at least one interior angle is greater than 180 degrees).
Therefore, the given quadrilateral, based on its properties and symmetry, is a convex deltoid.
Answer
Convex deltoid
Exercise #2
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve this problem, let's analyze the given quadrilateral ABCD by examining its geometric properties:
- Step 1: Identifying characteristics of a deltoid
A deltoid, or kite, is a quadrilateral that has two distinct pairs of adjacent sides that are equal. To classify a shape as a deltoid, we need to verify these properties. - Step 2: Examining the quadrilateral ABCD
The deltoid can be either concave or convex. If the shape is concave, it will have an indentation, meaning at least one angle is greater than . A convex deltoid does not have such an indentation. - Step 3: Analyze the sides of ABCD
Looking at the segments from the given points:
- Verify if pairs of adjacent sides are equal.
If we cannot find two equal pairs of adjacent sides, the quadrilateral is not a deltoid. - Step 4: Drawing conclusions
Having analyzed the sides of the quadrilateral, if none of the pairs of adjacent sides conform to the deltoid property as outlined—two pairs of equal adjacent sides—then ABCD is identified as not a deltoid.
Therefore, the correct answer is: Not deltoid.
Answer
Not deltoid
Exercise #3
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve this problem, let's analyze the quadrilateral depicted:
- Step 1: Analyze the given quadrilateral's shape using its geometric features, noting potential symmetry and side equivalence.
- Step 2: Identify if the quadrilateral fulfills the characteristics of a deltoid, which involve pairs of adjacent sides being equal.
- Step 3: Determine if it is possible to accurately categorize the quadrilateral as a convex or concave deltoid based on the given image and without explicit measurements.
- Step 4: In the absence of direct measurable evidence, consider if categorization is feasible.
Assessing visuals alone can lead to assumptions about equal lengths or angles, but without numerical data, it's challenging to make definitive geometrical claims about sides or symmetry.
Given these limitations, it is reasonable to conclude that we cannot definitively prove whether the quadrilateral is a deltoid (convex or concave) using just the visual representation provided.
Therefore, the solution to the problem is "It is not possible to prove if it is a deltoid or not."
Answer
It is not possible to prove if it is a deltoid or not
Exercise #4
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
The problem requires determining if a given quadrilateral is a deltoid, and if so, whether it is convex, concave, or indeterminate based on the provided diagram. A deltoid, or kite, is generally defined as a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides being of equal length. Thus, a visual analysis is essential here as only diagrammatic data is available.
To address this, one must closely analyze the properties of the given quadrilateral in terms of similarity and its symmetry relative to a conventional deltoid structure:
- Typically, you'd look for simultaneous symmetry or patterns indicating two equal-length adjacent pairs of sides.
- After examining the diagram and the naming convention (vertices labelled A, B, C, D), see if it implies any such congruency visually or through label symmetry.
- Lack of distinct clues for equal side pairs or diagonals prevents concluding its specific nature without additional information, especially since no specific length measures or angles are provided.
Given this and under diagram-only conditions, it's not possible to definitively prove that the shape is completely a deltoid (convex or concave). Therefore, without further data, identifying the indicated quadrilateral deltoid nature is beyond determining from the given data itself.
Consequently, the correct answer is: It is not possible to prove if it is a deltoid or not.
Answer
It is not possible to prove if it is a deltoid or not
Exercise #5
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
To solve this problem, let's examine the properties of the given quadrilateral:
- Step 1: Identify if the quadrilateral has any interior angles greater than .
- Step 2: Verify if the quadrilateral has two pairs of contiguous equal-length sides, which would qualify it as a deltoid (kite).
- Step 3: Determine whether the shape is concave or convex based on the angles and diagonal layout.
Analysis: In the provided diagram, the quadrilateral has a vertex that forms an interconnecting internal angle greater than , showing that it's a concave shape. The sides and suggest two pairs of contiguous equal sides.
Based on the properties identified:
- One angle exceeds , indicating a concave form.
- It has two sets of adjacent sides that are equal, confirming it as a deltoid.
Therefore, the shape shown in the illustration matches the properties of a concave deltoid.
The correct answer is thus Concave deltoid.
Answer
Concave deltoid
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
Indicate the correct answer
The next quadrilateral is:
More Questions
Area of a Deltoid
- Calculate Triangle Ratios in a Deltoid: Using the 1:5 Point Relationship
- Deltoid Geometry: Calculate the 1:3 Point Division and Triangle Area Ratio
- Deltoid Area Calculation: Using 4cm and 5cm Diagonals
- Deltoid Diagonal Calculation: Finding AC When Area = 24cm² and DB = 4
- Calculate the Second Diagonal in a Deltoid with Area 18 cm² and First Diagonal 3 cm
- Area
- Trapezoids
- Area of a trapezoid
- Perimeter of a trapezoid
- Parallelogram
- The area of a parallelogram: what is it and how is it calculated?
- Perimeter of a Parallelogram
- Kite
- Rectangle
- Calculating the Area of a Rectangle
- The perimeter of the rectangle
- Congruent Rectangles
- The sides or edges of a triangle
- Triangle Height
- The Sum of the Interior Angles of a Triangle
- Exterior angles of a triangle
- Rhombus, kite, or diamond?
- The Area of a Rhombus
- Perimeter
- Triangle
- Types of Triangles
- Obtuse Triangle
- Equilateral triangle
- Identification of an Isosceles Triangle
- Scalene triangle
- Acute triangle
- Isosceles triangle
- The Area of a Triangle
- Area of a right triangle
- Area of Isosceles Triangles
- Area of a Scalene Triangle
- Area of Equilateral Triangles
- Perimeter of a triangle
- Areas of Polygons for 7th Grade
- Right Triangle
- Area of a right-angled trapezoid
- Area of an isosceles trapezoid
- Median in a triangle
- Center of a Triangle - The Centroid - The Intersection Point of Medians
- How do we calculate the area of complex shapes?
- How to calculate the area of a triangle using trigonometry?
- How do we calculate the perimeter of polygons?
- All terms in triangle calculation
- Symmetry in a kite