An acute triangle has all acute angles, meaning each of its three angles measures less than degrees and the sum of all three together equals degrees.
Acute triangle
Test yourself on types of triangles!
In a right triangle, the side opposite the right angle is called....?
Next, we will look at some examples of acute triangles:
Acute triangle
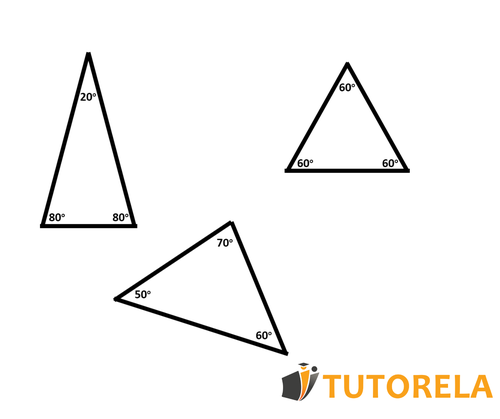
3 Examples of acute triangles
Exercises with Acute Triangles
Exercise 1
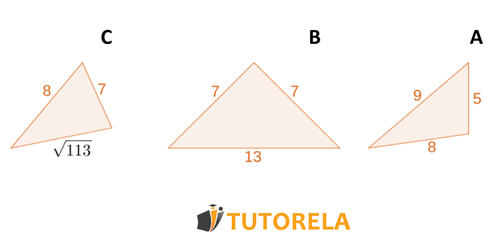
Assignment:
Determine which of the following triangles is obtuse, which is acute, and which is a right triangle:
Solution:
A. We will examine if the Pythagorean theorem holds for this triangle:
The sum of the squares of the perpendicular sides is greater than the square of the remaining side, therefore it is an acute-angled triangle.
B. Now we will examine this triangle:
The sum of the squares of the perpendicular sides is greater than the square of the remaining side, therefore it is an obtuse-angled triangle.
C. The longest side of the 3 will be treated as the hypotenuse.
The Pythagorean theorem holds true and therefore triangle 3 is a right triangle.
Answer:
A-acute angle acute B-obtuse angle obtuse C-right angle right.
In an isosceles triangle, what are each of the two equal sides called ?
In a right triangle, the two sides that form a right angle are called...?
Does the diagram show an obtuse triangle?
Exercise 2
Let's look at 3 angles
Angle A is equal to
Angle B is equal to
Angle C is equal to
Task:
Can these angles form a triangle?
Solution:
The sum of the angles in a triangle is equal to ,
therefore these angles can form a triangle.
Answer:
Yes, since the sum of the internal angles of a triangle is equal to .
Exercise 3
Angle A is equal to
Angle B is equal to
Angle C is equal to
Task:
Can these angles form a triangle?
Solution:
The sum of the angles is greater than ,
therefore these angles cannot form a triangle.
Answer:
No, since the sum of the internal angles must be , and in this case the angles add up to .
Examples and exercises with solutions for acute triangles
Exercise #1
In a right triangle, the side opposite the right angle is called....?
Step-by-Step Solution
The problem requires us to identify the side of a right triangle that is opposite to its right angle.
In right triangles, one of the most crucial elements to recognize is the presence of a right angle (90 degrees).
The side that is directly across or opposite the right angle is known as the hypotenuse. It is also the longest side of a right triangle.
Therefore, when asked for the side opposite the right angle in a right triangle, the correct term is the hypotenuse.
Selection from the given choices corroborates our analysis:
- Choice 1: Leg - In the context of right triangles, the "legs" are the two sides that form the right angle, not the side opposite to it.
- Choice 2: Hypotenuse - This is the correct identification for the side opposite the right angle.
Therefore, the correct answer is .
Answer
Hypotenuse
Exercise #2
In an isosceles triangle, what are each of the two equal sides called ?
Step-by-Step Solution
In an isosceles triangle, there are three sides: two sides of equal length and one distinct side. Our task is to identify what the equal sides are called.
To address this, let's review the basic properties of an isosceles triangle:
- An isosceles triangle is defined as a triangle with at least two sides of equal length.
- The side that is different in length from the other two is usually called the "base" of the triangle.
- The two equal sides of an isosceles triangle are referred to as the "legs."
Therefore, each of the two equal sides in an isosceles triangle is called a "leg."
In our problem, we confirm that the correct terminology for these two equal sides is indeed "legs," distinguishing them from the "base," which is the unequal side. This aligns with both the typical definitions and properties of an isosceles triangle.
Thus, the equal sides in an isosceles triangle are known as legs.
Answer
Legs
Exercise #3
In a right triangle, the two sides that form a right angle are called...?
Step-by-Step Solution
In a right triangle, there are specific terms for the sides. The two sides that form the right angle are referred to as the legs of the triangle. To differentiate, the side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse, which is distinct due to being the longest side. Hence, in response to the problem, the sides forming the right angle are correctly identified as Legs.
Answer
Legs
Exercise #4
Does the diagram show an obtuse triangle?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
To determine if the triangle in the diagram is obtuse, we will visually assess the angles:
- Step 1: Identify the angles in the diagram. The triangle has three angles, with one angle appearing between the horizontal base and the left slanted side.
- Step 2: Evaluate the angle between the base and the left side. If it opens wider than a right angle, it's considered obtuse. This angle seems to be greater than , indicating obtuseness.
- Step 3: Conclude based on visual inspection. Since this key angle is greater than , the triangle must be an obtuse triangle.
Therefore, the solution to the problem is Yes; the diagram does show an obtuse triangle.
Answer
Yes
Exercise #5
Does the diagram show an obtuse triangle?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
To determine if the triangle shown in the diagram is obtuse, we proceed as follows:
- Step 1: Identify that the diagram is indeed a triangle by observing the confluence of three edges forming a closed shape.
- Step 2: Appreciate the geometric arrangement of the triangle, focusing on the sides' lengths and angles visually.
- Step 3: Noticeably, the longest side of the triangle represents a noticeable tilt indicating the presence of an obtuse angle.
Based on the observation above, notably from the triangle's longest side against the base, it's clear that one angle is larger than . Hence, the triangle in the diagram is indeed an obtuse triangle.
Therefore, the correct answer is Yes.
Answer
Yes
Does the diagram show an obtuse triangle?
Given the values of the sides of a triangle, is it a triangle with different sides?
Given the values of the sides of a triangle, is it a triangle with different sides?
More Questions
Types of Triangles
- Parallel Line Geometry: Classifying Triangle ABC with Extended Side AE
- Right Triangle Area Problem: Solve for X When Area = 6 cm²
- Triangle Classification: Identifying a Right Triangle with 90-Degree Angle
- Triangle Classification: Identifying a Shape with 70°, 70°, and 40° Angles
- Triangle Classification: Determine Type with Angles 39°, 107°, and 34°
- Area
- Trapezoids
- Area of a trapezoid
- Perimeter of a trapezoid
- Parallelogram
- The area of a parallelogram: what is it and how is it calculated?
- Perimeter of a Parallelogram
- Kite
- Area of a Deltoid (Kite)
- Congruent Triangles
- Angles In Parallel Lines
- Alternate angles
- Corresponding angles
- Collateral angles
- Vertically Opposite Angles
- Adjacent angles
- The Pythagorean Theorem
- Elements of the circumference
- Circle
- Diameter
- Pi
- Area of a circle
- The Circumference of a Circle
- The Center of a Circle
- Radius
- How is the radius calculated using its circumference?
- Rectangle
- Calculating the Area of a Rectangle
- The perimeter of the rectangle
- Congruent Rectangles
- The sides or edges of a triangle
- Similarity of Triangles and Polygons
- Triangle similarity criteria
- Triangle Height
- Midsegment
- Midsegment of a triangle
- The Sum of the Interior Angles of a Triangle
- Exterior angles of a triangle
- Relationships Between Angles and Sides of the Triangle
- Relations Between The Sides of a Triangle
- Rhombus, kite, or diamond?
- The Area of a Rhombus
- Perimeter
- Triangle
- The Area of a Triangle
- Area of a right triangle
- Area of Isosceles Triangles
- Area of a Scalene Triangle
- Area of Equilateral Triangles
- Perimeter of a triangle
- Right Triangular Prism
- Bases of the Right Triangular Prism
- The lateral faces of the prism
- Lateral Edges of a Prism
- Height of a Prism
- The volume of the prism
- Surface area of triangular prisms
- Areas of Polygons for 7th Grade
- Area of a right-angled trapezoid
- Area of an isosceles trapezoid
- Corresponding exterior angles
- Alternate interior angles
- Median in a triangle
- Center of a Triangle - The Centroid - The Intersection Point of Medians
- How do we calculate the area of complex shapes?
- How to calculate the area of a triangle using trigonometry?
- How do we calculate the perimeter of polygons?
- All terms in triangle calculation
- Parts of a Circle