There is a wide variety of geometric shapes, which you can read about in detail:
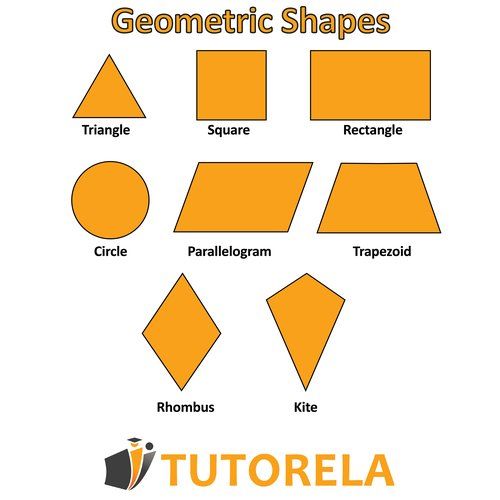
Geometric shapes
Test yourself on triangle!
Angle A is equal to 30°.
Angle B is equal to 60°.
Angle C is equal to 90°.
Can these angles form a triangle?
Geometric shapes
triangle
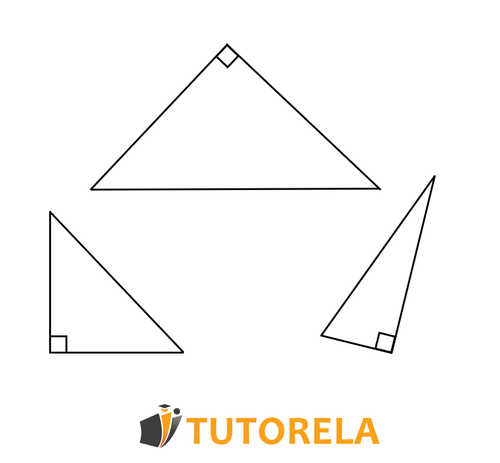
A triangle is a geometric shape with sides. In every triangle, the sum of angles equals .
Below are the different types of triangles –
- Equilateral triangle - a triangle in which all sides are equal, all angles are equal, and every height is also a median and an angle bisector.
- Isosceles triangle - a triangle in which two legs are equal, two base angles are equal, and the median to the base is also the height and the vertex angle bisector.
- Right triangle - a triangle with one angle of degrees formed by two legs. The side opposite to the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
- Scalene triangle - a triangle in which all sides are different from each other.
Rectangle
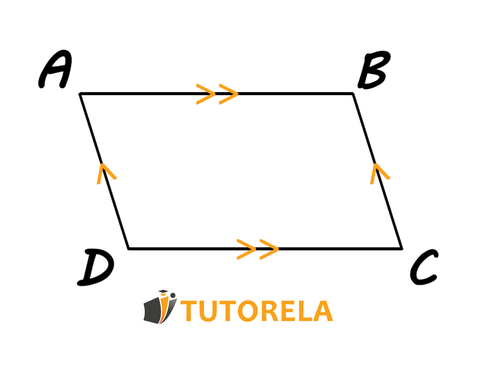
A rectangle is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel opposite sides.
It can also be defined as a parallelogram with a degree angle.
Since a rectangle is a type of parallelogram, it has all the properties of a parallelogram.

Here are the properties of a rectangle:
- Every pair of opposite sides are equal and parallel.
- All angles in a rectangle are equal to degrees.
- The diagonals of a rectangle are equal to each other.
- The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other (divide each other in half, not just intersect).
- Since both diagonals are equal, all halves of the diagonals are equal.
- The diagonals of a rectangle are not perpendicular to each other and do not bisect the angles of the rectangle.
Angle A equals 56°.
Angle B equals 89°.
Angle C equals 17°.
Can these angles make a triangle?
Angle A equals 90°.
Angle B equals 115°.
Angle C equals 35°.
Can these angles form a triangle?
Look at the rectangle ABCD below.
Side AB is 6 cm long and side BC is 4 cm long.
What is the area of the rectangle?
Trapezoid
A general trapezoid is a trapezoid where two of its opposite sides are parallel and are called the bases of the trapezoid.
The other two sides are called the legs of the trapezoid, and they are not parallel and face different directions.

Meet the basic properties of a trapezoid:
• Two sides are parallel to each other
• The sum of the angles that lean on the same leg (one from the small base and the other from the large base) is degrees.
• If we draw a diagonal that intersects both bases, it will create equal alternate angles between parallel lines.
• The sum of all angles in a trapezoid equals degrees.
• If we draw a segment that passes exactly through the middle of the legs of the trapezoid, we obtain a segment that is parallel to the bases and equal to half their sum.
Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with pairs of parallel sides.
How to prove a parallelogram:
- First way:
If in a quadrilateral every pair of opposite sides are parallel to each other, the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. - Second way:
If in a quadrilateral every pair of opposite sides are equal to each other, the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. - Third way:
If in a quadrilateral there is one pair of opposite sides that are both equal and parallel, the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. - Fourth way:
If in a quadrilateral, the diagonals bisect each other, the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. - Fifth way:
If in a quadrilateral there are two pairs of equal opposite angles, the quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
Given the rhombus in the drawing:
What is the area?
Look at the deltoid in the figure:
What is its area?
Look at the rectangle ABCD below.
Side AB is 4.5 cm long and side BC is 2 cm long.
What is the area of the rectangle?
kite
A kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent equal sides.
To better understand this, imagine that a kite is composed of two isosceles triangles joined together.
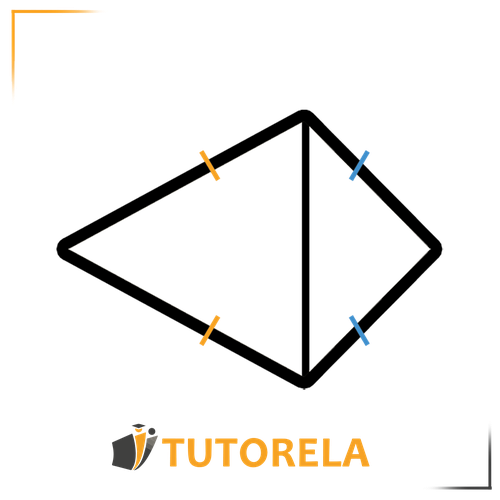
Here are the main properties of the kite:
The main diagonal in a kite, which extends from the two vertices of the triangles, is both an angle bisector, a median, and perpendicular to the secondary diagonal, which extends from the base angles of the triangles.
Click here to learn more about kites.
rhombus
A rhombus is a parallelogram with a pair of adjacent sides that are equal.
Here are the properties of a rhombus:
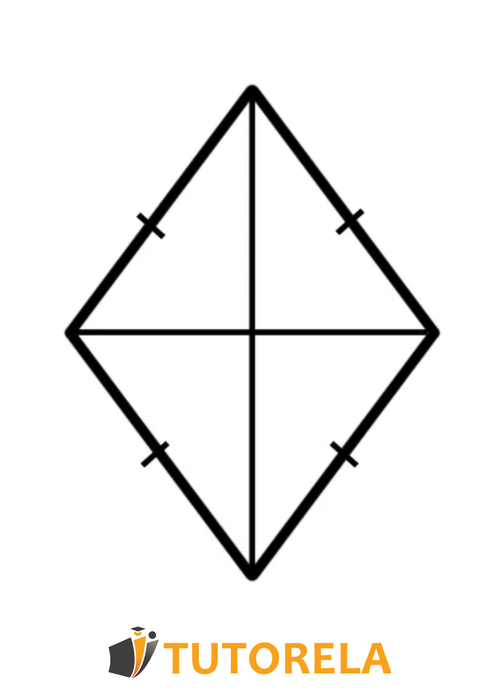
- In a rhombus, all sides are equal.
- In a rhombus, there are two pairs of parallel opposite sides.
- In a rhombus, adjacent angles sum to degrees.
- The sum of angles is degrees.
- In a rhombus, there are two pairs of equal opposite angles.
Given the trapezoid:
What is the area?
Look at the rectangle below.
Side AB is 2 cm long and side BC has a length of 7 cm.
What is the perimeter of the rectangle?
Look at the trapezoid in the figure.
Calculate its perimeter.
Examples with solutions for Triangle
Exercise #1
Angle A is equal to 30°.
Angle B is equal to 60°.
Angle C is equal to 90°.
Can these angles form a triangle?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
We must first add the three angles to see if they equal 180 degrees:
The sum of the angles equals 180, therefore they can form a triangle.
Answer
Yes
Exercise #2
Angle A equals 56°.
Angle B equals 89°.
Angle C equals 17°.
Can these angles make a triangle?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
We add the three angles to see if they are equal to 180 degrees:
The sum of the given angles is not equal to 180, so they cannot form a triangle.
Answer
No.
Exercise #3
Angle A equals 90°.
Angle B equals 115°.
Angle C equals 35°.
Can these angles form a triangle?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
We add the three angles to see if they are equal to 180 degrees:
The sum of the given angles is not equal to 180, so they cannot form a triangle.
Answer
No.
Exercise #4
Look at the rectangle ABCD below.
Side AB is 6 cm long and side BC is 4 cm long.
What is the area of the rectangle?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
Remember that the formula for the area of a rectangle is width times height
We are given that the width of the rectangle is 6
and that the length of the rectangle is 4
Therefore we calculate:
6*4=24
Answer
24 cm²
Exercise #5
Given the rhombus in the drawing:
What is the area?
Video Solution
Step-by-Step Solution
Let's remember that there are two ways to calculate the area of a rhombus:
The first is the side times the height of the side.
The second is diagonal times diagonal divided by 2.
Since we are given both diagonals, we calculate it the second way:
Answer
14
More Questions
Rectangles
- Calculate Rectangle Perimeter: Finding the Total Length of a 4.8 cm × 12 cm Rectangle
- Calculate the Perimeter: Finding Border Length in a 2×4×5 Rectangular Diagram
- Rectangle Area Problem: Finding BC When AB = 5cm and Area = 30cm²
- Calculate Rectangle Area: Finding the Space of a 10 cm × 2.5 cm Rectangle ABCD
- Calculate Rectangle Side Length: Given Area 42 cm² and Height 12 cm
Deltoid
- Calculate Triangle Ratios in a Deltoid: Using the 1:5 Point Relationship
- Deltoid Geometry: Calculate the 1:3 Point Division and Triangle Area Ratio
- Deltoid Area Calculation: Using 4cm and 5cm Diagonals
- Deltoid Diagonal Calculation: Finding AC When Area = 24cm² and DB = 4
- Calculate the Second Diagonal in a Deltoid with Area 18 cm² and First Diagonal 3 cm
Triangle
- Triangle Classification: Analyzing Angles 53°, 117°, and 21°
- Isosceles Triangle ABC with Parallel Line ED: Investigating Triangle Properties
- Triangle Classification: Identifying a Shape with Three 60° Angles
- Calculate Triangle Area: Paint Coverage in 6-Meter Square Playground
- Calculate Triangle Perimeter: Finding the Sum of Sides 6, 8, and 10
Parallelogram
- Calculate Parallelogram Area: 90° Perpendicular Height and 40-Unit Side
- Parallelogram Area Calculation: Using Height CE and Segments 5, 7, and 2
- Calculate Parallelogram Area: Rectangle with Perimeter 24 Inside
- Calculate Parallelogram Area: Circle with Circumference 25.13 and Tangent Points
- Circle-Parallelogram Tangency Problem: Finding Area of Blue Regions with 25.13 Circumference
Trapeze
- Calculate Trapezoid Height: Given Area 30 and Parallel Sides 6 and 9
- Calculate the Area of an Equilateral Hexagon with Side Length 7 and Height 12.124
- Calculate Trapezoid Area: Isosceles Triangle with Height 8 and Base 17
- Calculate Trapezoid Perimeter: Inside an Isosceles Triangle with Height 8
- Trapezoid Area Calculation: Verifying and Applying the Formula with 4cm and 7cm Parallel Sides
- Area
- Trapezoids
- Symmetry in Trapezoids
- Diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid
- Area of a trapezoid
- Perimeter of a trapezoid
- Types of Trapezoids
- Isosceles Trapezoid
- Parallelogram
- The area of a parallelogram: what is it and how is it calculated?
- Perimeter of a Parallelogram
- Kite
- Area of a Deltoid (Kite)
- Congruent Triangles
- Congruence Criterion: Side, Angle, Side
- Congruence Criterion: Angle, Side, Angle
- Congruence Criterion: Side, Side, Side
- Congruence of Right Triangles (using the Pythagorean Theorem)
- The Pythagorean Theorem
- The Application of the Pythagorean Theorem to an Orthohedron or Cuboid
- Rectangle
- From a Quadrilateral to a Rectangle
- From a Parallelogram to a Rectangle
- Calculating the Area of a Rectangle
- The perimeter of the rectangle
- Congruent Rectangles
- The sides or edges of a triangle
- Similarity of Triangles and Polygons
- Similarity of Geometric Figures
- Similarity ratio
- Similar Triangles
- Triangle similarity criteria
- Triangle Height
- The Sum of the Interior Angles of a Triangle
- Exterior angles of a triangle
- Relationships Between Angles and Sides of the Triangle
- Relations Between The Sides of a Triangle
- Rhombus, kite, or diamond?
- Diagonals of a Rhombus
- Lines of Symmetry in a Rhombus
- From Parallelogram to Rhombus
- The Area of a Rhombus
- Perimeter
- Triangle
- Types of Triangles
- Obtuse Triangle
- Equilateral triangle
- Identification of an Isosceles Triangle
- Scalene triangle
- Acute triangle
- Isosceles triangle
- The Area of a Triangle
- Area of a right triangle
- Area of Isosceles Triangles
- Area of a Scalene Triangle
- Area of Equilateral Triangles
- Perimeter of a triangle
- Right Triangular Prism
- Bases of the Right Triangular Prism
- The lateral faces of the prism
- Lateral Edges of a Prism
- Height of a Prism
- The volume of the prism
- Surface area of triangular prisms
- Areas of Polygons for 7th Grade
- Right Triangle
- Area of a right-angled trapezoid
- Area of an isosceles trapezoid
- Median in a triangle
- Center of a Triangle - The Centroid - The Intersection Point of Medians
- How do we calculate the area of complex shapes?
- How to calculate the area of a triangle using trigonometry?
- How do we calculate the perimeter of polygons?
- All terms in triangle calculation
- Diagonals in a rectangle
- Symmetry in a kite